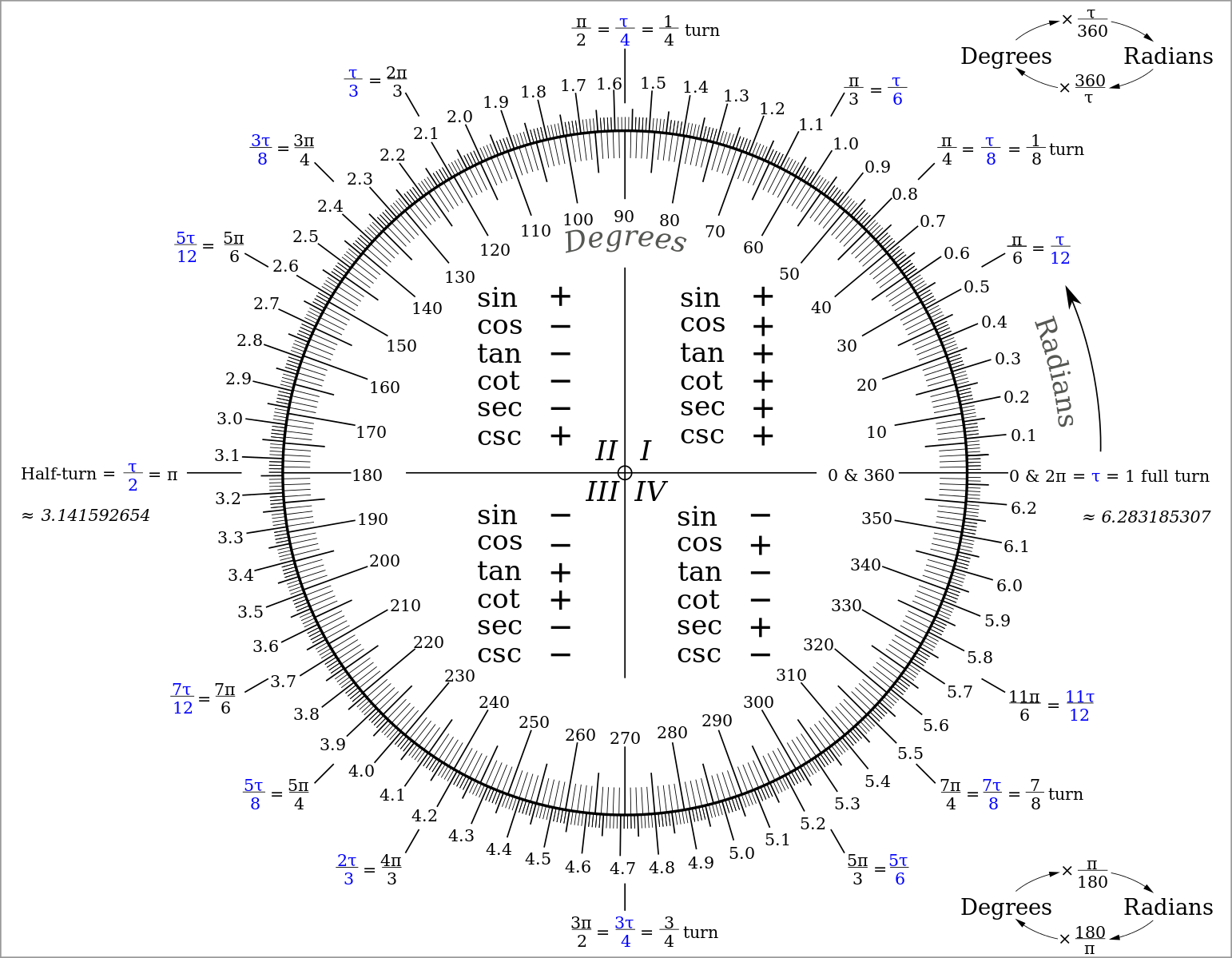
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world onThus, the measure of angle θ in radians equals onefourth the total circumference, or π/2 (about 157) The measure of angle θ can also be represented in degrees By definition, a circle has 360 degrees, so θ equals 90 degrees (90°) The following table shows angle measures represented in degrees and radiansReturns Double An angle, θ, measured in radians, such that π ≤ θ ≤ π, and tan(θ) = y / x, where (x, y) is a point in the Cartesian planeObserve the following For (x, y) in quadrant 1, 0 < θ < π/2For (x, y) in quadrant 2, π/2 < θ ≤ πFor (x, y) in quadrant 3, π < θ < π/2For (x, y) in quadrant 4, π/2 < θ < 0For points on the boundaries of the quadrants, the return

42 Printable Unit Circle Charts Diagrams Sin Cos Tan Cot Etc
What is 5 pi over 2 in degrees
What is 5 pi over 2 in degrees-Here, we use the formula Radians = (Degrees × π)/180° Radians = (90° × π)/180° = π/2 = 0785 rad Thus, a right angle is expressed as π/2 radians What Are 60 Degrees Converted to Radians?Degrees and Radians Converting special angles between degrees and exact radians This activity was created by a Quia Web subscriber




Ex 3 1 2 Find Degree Of Radian Measures 11 16 4 Ex 3 1
Step 1 Write the numerical value of measure of angle given in degrees Step 2 Now, multiply the numeral value written in the step 1 by π/180 Step 3 Simplify the expression by cancelling the common factors of the numerical Step 4 The result obtained after the simplification will beA reference angle is the acute version of any angle determined by repeatedly subtracting or adding straight angle (1 / 2 turn, 180°, or π radians), to the results as necessary, until the magnitude of the result is an acute angle, a value between 0 and 1 / 4 turn, 90°, or π / 2 radians For example, an angle of 30 degrees has a reference angle of 30 degrees, and an angle of 150 degrees also has a reference angle of 30 degreesStart studying Pre Calculus Radians and Degrees Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools
In a half circle there are π radians, which is also 180° π radians = 180° So 1 radian = 180°/π = ° (approximately) To go from radians to degrees multiply by 180, divide by π To go from degrees to radians multiply by π, divide by 180 Here is a table of equivalent values DegreesStart studying radians & degrees (45) Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsTrigonometry (from Greek trigōnon, "triangle" and metron, "measure") is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles
Answer π/2 = 90° Stepbystep explanation Given that, Radian measure = π/2 The formula used to convert radian measure to degree measure is given byThus, the sine of angle α is a ratio of the length of the opposite side,BC to the angle α and its hypotenuse AB Sin α = = = BC/AB So, sin 45 degrees trigonometry value, infraction will be, sin 45° = A simple method by means of which we can calculate the value of sine ratios for all the degrees is discussed here(m/s) over (m/s 2)




10 2 Angles And Their Measure Mathematics Libretexts




Explicit Function Which Is Tan X Pi 2 X Pi 2 Rotated By For Example 45 Degrees Anticlockwise About Origin Mathematics Stack Exchange
Then multiply the measurement in radians by 180 divided by pi For example, pi over 3 radians would be equal to 60 degrees If the measurement is 2 radians, remember that it does not include pi, and multiply 2 by 180 divided by pi to get 1145 degrees For more examples of converting radians to degrees, read on!Our tool displays ten The returned angle is given in radians in the range π/2 to π/2 The Atan2 function returns the arctangent, or inverse tangent, of the specified x and y coordinates as arguments The arctangent is the angle from the x axis to a line that contains the origin (0, 0) and a point with coordinates ( x , y )




Radian Measure Gamma Maths Chapter33 Radians To Degrees Degrees To Radians Angle And Sector Area Ppt Download




What Is An Acute Angle Learn The Definition Of Acute Angle And How To Find Acute Angles In Real Life Review Some Acute Angle Examples And Acute Angle Shapes
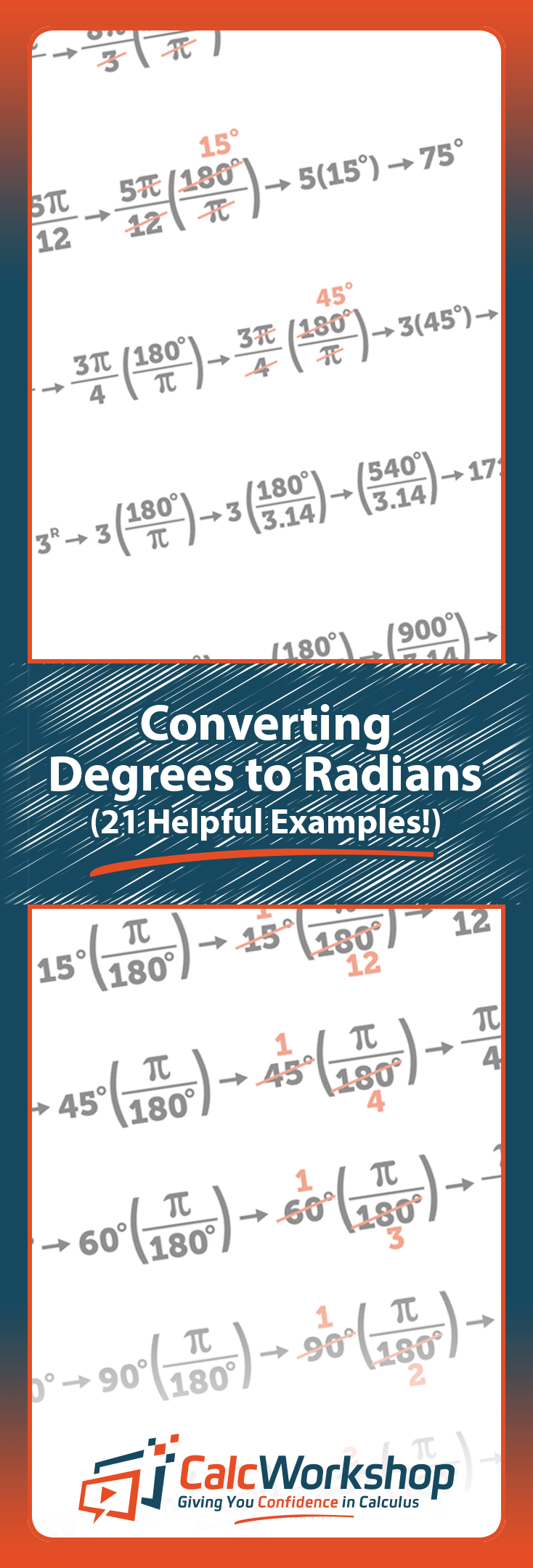
Degrees And Radians Conversion Solutions Examples Videos, Converting Radians To Degrees And Degrees To Radians, Degrees Degrees And Radians Conversion Practice, Degrees And Radians Worksheets Conversion Of Angle Measures, How To Convert Between Radians And Degrees Math Print Converting, How To Convert Radians To Degrees 4 Steps With Pictures, Conversion Between DegreesThe sine is a trigonometric function of an angle, usually defined for acute angles within a rightangled triangle as the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the longest side of the triangle In the illustration below, sin (α) = a/c and sin (β) = b/c From cos (α) = a/c follows that the sine of any angle is always less than or equalSteps Step 1 Plug the angle value, in degrees, in the formula above radian measure = (25 × π)/180 Step 2 Rearrange the terms radian measure = π × 25/180 Step 3 Reduce or simplify the fraction of π if necessary Calculating the gcd of 25 and 180



The Circle Constant Scienceline



1
Trigonometry Graphing Trigonometric Functions Radian Measure 1 Answer Trevor Ryan #270^@# Explanation The conversion factor is #360^@=2pi rad# We may hence use this together with ratio and proportion to obtain that #(3pi)/2 radPlugging the angle value, in degrees, in the previous formula, we get α rad = π × 360 /180 = π × 360÷180/180÷180 = 2π radians, when reduced to lowest terms Note 2π rad can be expressed as real number or as a decimal as 2π rad = radiansAnswer and Explanation 1 We have sin( π 2 x) sin ( π 2 x) Applying the formula, we get sin(π 2 x) = sin π 2cosxcos π 2 sinx = 1⋅cosx0⋅sinx = cosx0 = cosx sin ( π 2




Uzivatel James Tanton Na Twitteru A Square Of Side 1 Meter Rotated 90 Degrees About Its Center Sweeps Out An Area Of P 2 M 2 A Cube Of Side 1 Rotated 90 Degrees



How To Convert Radians To Degrees 21 Amazing Examples
/ An application of 1genericity in the Π 2 0 enumeration degrees 9th Annual Conference on Theory and Applications of Models of Computation, TAMC 12, Beijing Vol 7287 LNCS Springer Verlag, 12 pp 6046The Key Point gives a list of angles measured in degrees on the left and the equivalent list in radians on the right It is important in mathematical work that you record correctly the unit of measure you are using Another useful relationship is given as follows π radians = 180 so 1 radian = 180 π degrees = (3 dp)Solution for Convert the angle π/2 in radians to degrees Social Science Anthropology



Radian Angles Quadrants Video Radians Khan Academy




Angles And Radian Measure Ppt Download
When x = π/2 or 90 degree y = sin 2 (90) cos 2 (90) = 1 Thus, for any value of x between π/2 and π/2, y is always 1 Graph H shows a line that has a constant value y = 1 for any value of x Ans H Share Comments Log In Advertisement (continue below) Groups mathematics 81 members Log In to join Maths Explanation × 1xradian = 180 π xdegrees ⇒ π 2 xradian = π 2 ⋅ 180 π xdegrees × × × × × x = 90xdegreesTo convert the result from radians to degrees, multiply the result by 180/PI() or use the DEGREES function For example, to convert the result of ATAN(1) to degrees, you can use either formula below Output of the function is limited to the range from π/2 to π/2 Images courtesy of wumbonet Related functions Excel ATAN2 Function




Ex 3 1 2 Find Degree Of Radian Measures 11 16 4 Ex 3 1
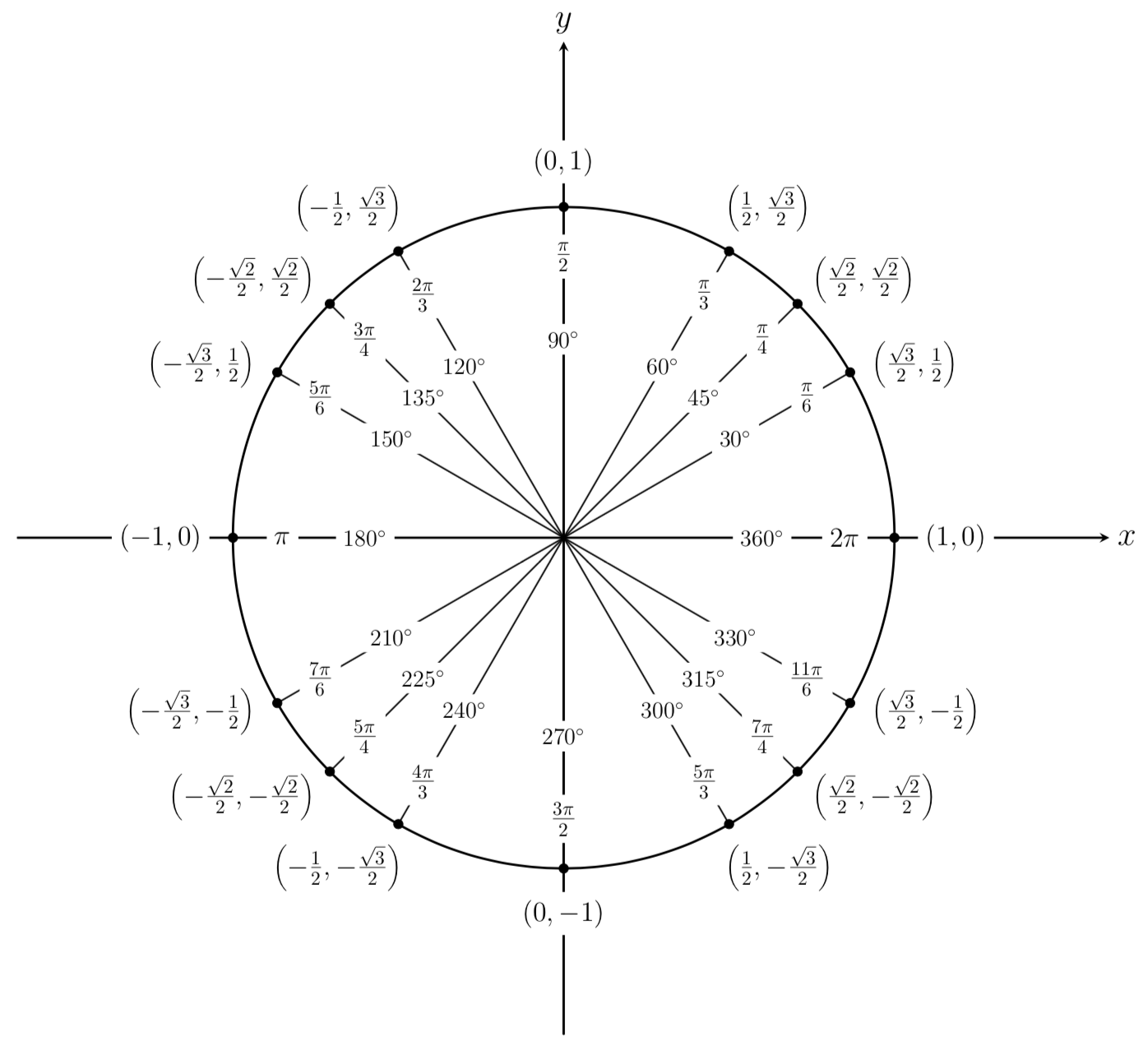



Mfg The Unit Circle
What is #(3pi)/2 # radians in degrees?If the angle measures 0 ∘ 0^\circ 0 ∘ in degrees, then the arc length of the circle carved out by the angle is 0 0 0 On the other hand, if the angle measures 36 0 ∘ 360^\circ 3 6 0 ∘ in degrees, then the arc length of the circle carved out by the angle is the circumference of a circle with radius 1 1 1, or 2 π ⋅ 1 = 2 π 2 \pi \cdot 1 = 2\pi 2 π ⋅ 1 = 2 πThe angle returned is between PI/2 and PI/2, ie π/2,π/2 Arguments Number is the real number, or a reference to a cell containing that number, must be from 1 to 1, whose inverse trigonometric sine value is to be calculated




Angular Size Coe College




Find The Degree Measure Corresponding To Following Radian Measures I 2pi 15 C Ii Pi 8 C Iii 2 C
The angle α in degrees is equal to the angle α in radians times 180 degrees divided by pi constant α (degrees) = α (radians) × 180° / π or degrees = radians × 180° / π Example Convert 2 radians angle to degrees α (degrees) = α (radians) × 180° / π = 2 × 180° / = ° Radians to degrees conversion tableThe csc of π/2 radians is 1, the same as csc of π/2 radians in degrees To change π/2 radians to degrees multiply π/2 by 180° / $\pi$ = 90° Csc π/2 = csc 90 degrees Our results of cscπ/2 have been rounded to five decimal places If you want cosecant π/2 with higher accuracy, then use the calculator below;You probably remember using fractions like π/2 = 90°, π/3 = 60°, π/4 = 45°, and π/6 = 30° back in trigonometry class When we talk about rotational motion, radians become the preferred unit of measure for angles



Find The Reference Angle For 8 Pi Divided By 5 Socratic




Convert Frac 2 P 3 Radians To Degrees A 60 Gauthmath
One steradian is equal to (180/π) 2 square degrees The concept of a solid angle and the term steradian can be perplexing to people only acquainted with ordinary angles Everybody knows what a 90° angle looks like and even referring to it as π/2 radians is relatively easy to understand But it is a different matter altogether with solidCosine of 90 degrees compared to cosine of π/2 radians Open Live Script cosd(90) ans = 0 cos(pi/2) ans = e17 Cosine of complex angles specified in degrees Open Live Script Create an array of three complex angles and compute the cosine zA degree (in full, a degree of arc, arc degree, or arcdegree), usually denoted by ° (the degree symbol), is a measurement of a plane angle in which one full rotation is 360 degrees It is not an SI unit—the SI unit of angular measure is the radian—but it is mentioned in the SI brochure as an accepted unit Because a full rotation equals 2π radians, one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians
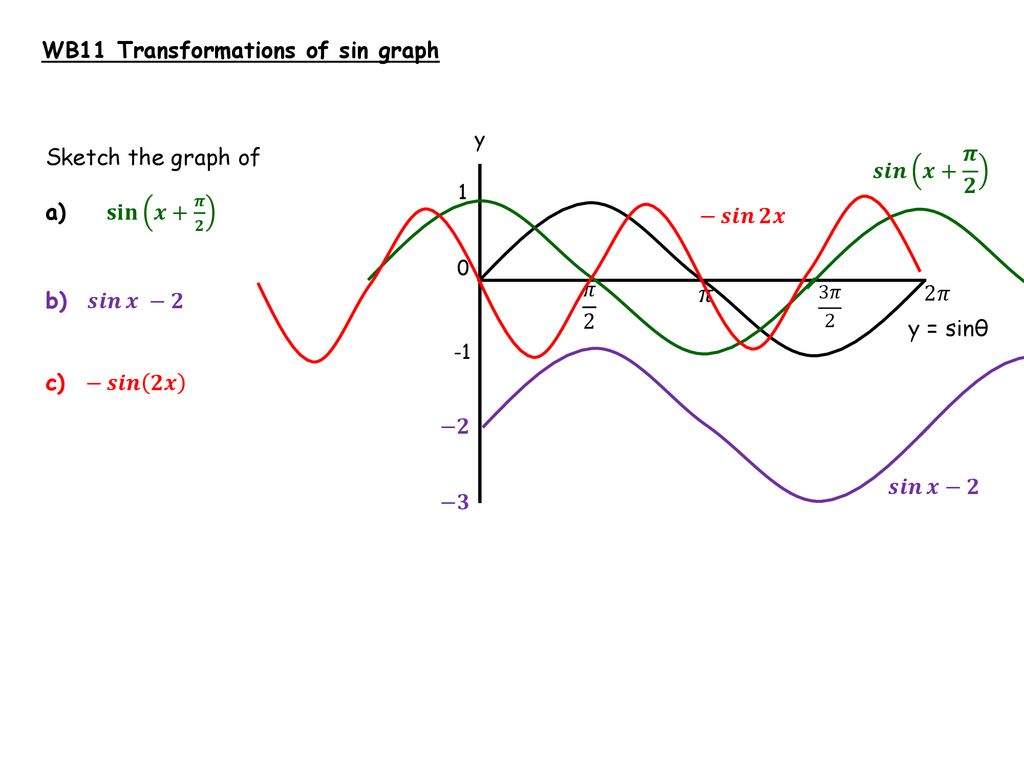



Trig Graphs And Equations Ppt Download




Degrees To Radians Video Trigonometry Khan Academy
The csc of π/2 radians is 1, the same as csc of π/2 radians in degrees To change π/2 radians to degrees multiply π/2 by 180° / $\pi$ = 90° Csc π/2 = csc 90 degrees Our results of cscπ/2 have been rounded to five decimal places If you want cosecant π/2 with higher accuracy, then use the calculator below;Argument is a metric representing a list of values to be converted from radians to degrees Example These simple examples illustrate how the Degrees function converts an angle entered in radians into degrees Function/Result Calculation Degrees(227) = 130 Degrees(π/2)Draw a unit circle with center as the origin Then if mathx= angle/math (measured anticlockwise) between between line joining origin and any point on the rim of the unit circle and the direction of positive xaxis, then mathcos(x)=Xcoordina
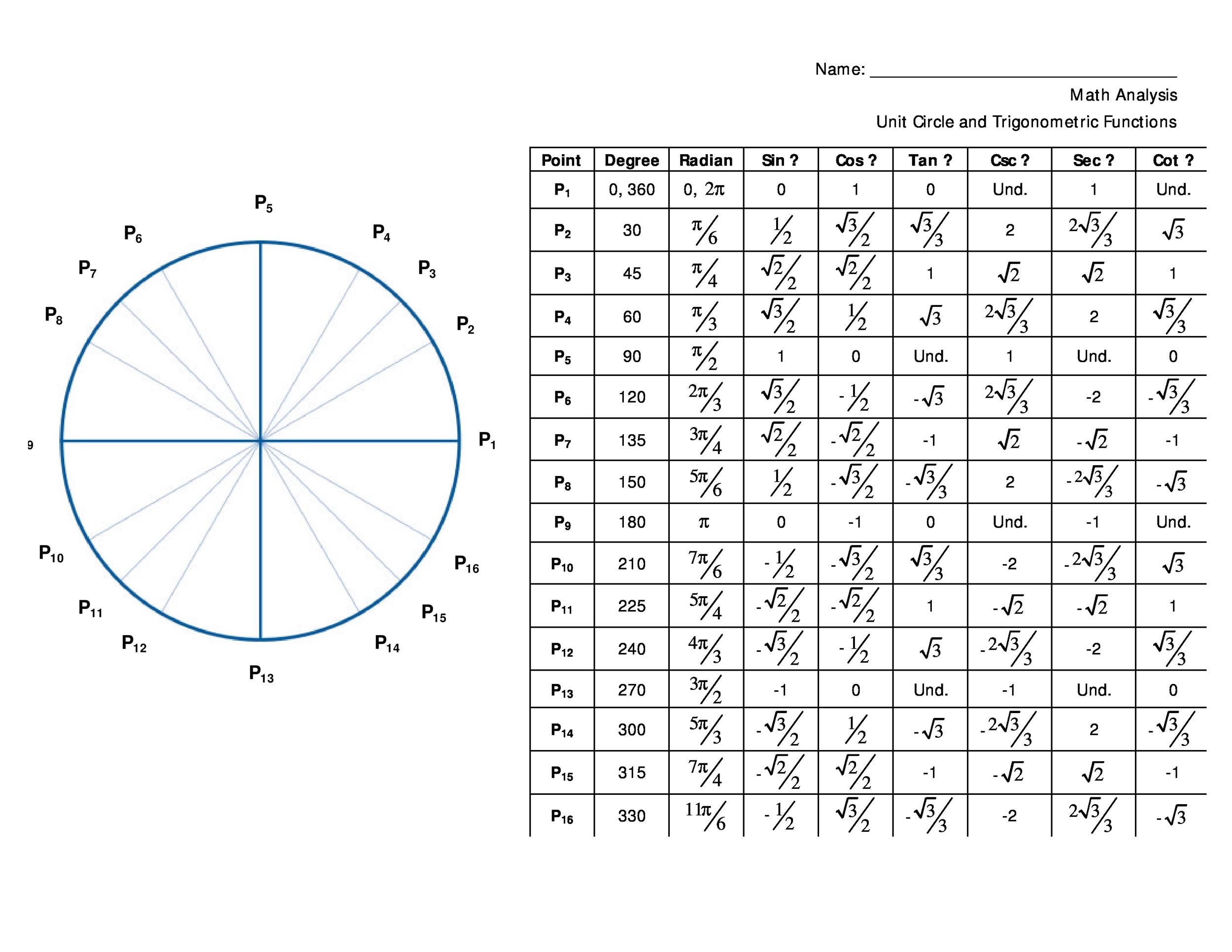



42 Printable Unit Circle Charts Diagrams Sin Cos Tan Cot Etc
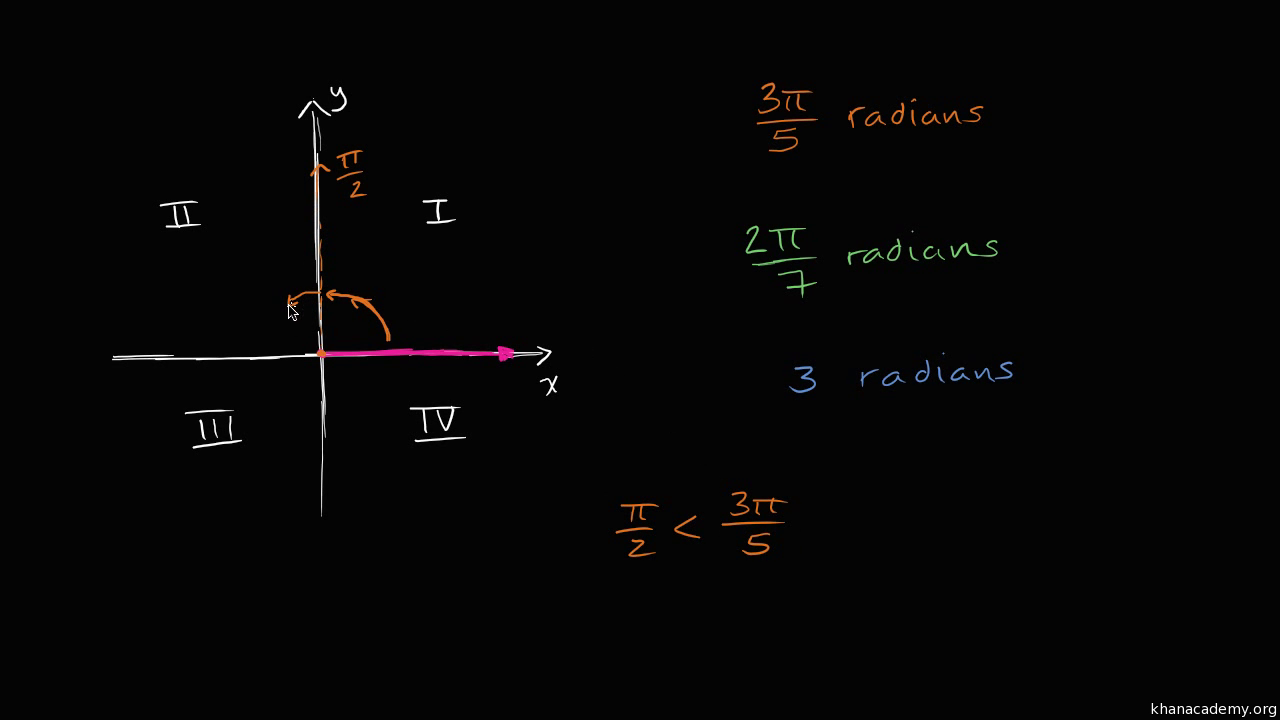



Radian Angles Quadrants Video Radians Khan Academy
Let us convert 60 degrees to radians, by multiplying the 60° angle by π/180° The formula used is Radians = (Degrees × π)/180°Convert from Radians to Degrees (3pi)/2 3π 2 3 π 2 To convert radians to degrees, multiply by 180 π 180 π, since a full circle is 360° 360 ° or 2π 2 π radians ( 3π 2)⋅ 180° π ( 3 π 2) ⋅ 180 ° π Cancel the common factor of π π Tap for more steps Factor π π out of 3 π 3 π π ⋅ Well, that would be when sin(θ) is the greatest at a value of π/2 (90 degrees you know, straight up) What about the units?
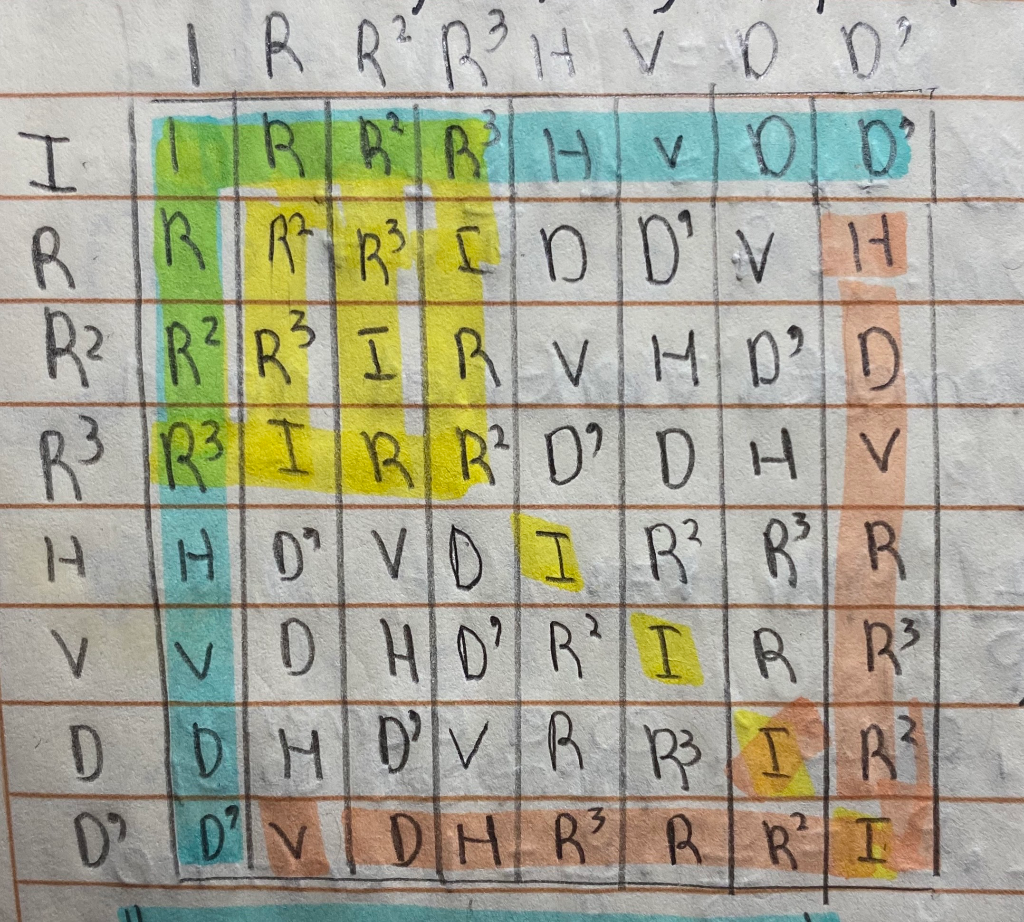



The Group D4 Of Isometries Of A Square D4 I Chegg Com




Argument Complex Analysis Wikipedia
Thus the measure of angle θ in radians equals onefourth the total circumference, or π/2 (about 157) The measure of angle θ can also be represented in degrees By definition, a circle has 360 degrees, so θ equals 90 degrees (90°) The following table shows angle measures represented in degrees and radiansOn the left, pi/2 is really radians Now we go off to the internet, and find that the conversion between degrees and radians is 1 radian = degrees Now multiply radians * degrees/radian and get 90 degrees (within the roundoff error ofDegrees radians90°π/2 not defined60°π/°π/4130°π/ 0° 0 0 30° π/6 45° π/4 1 60° π/3 90° π/2 not defined
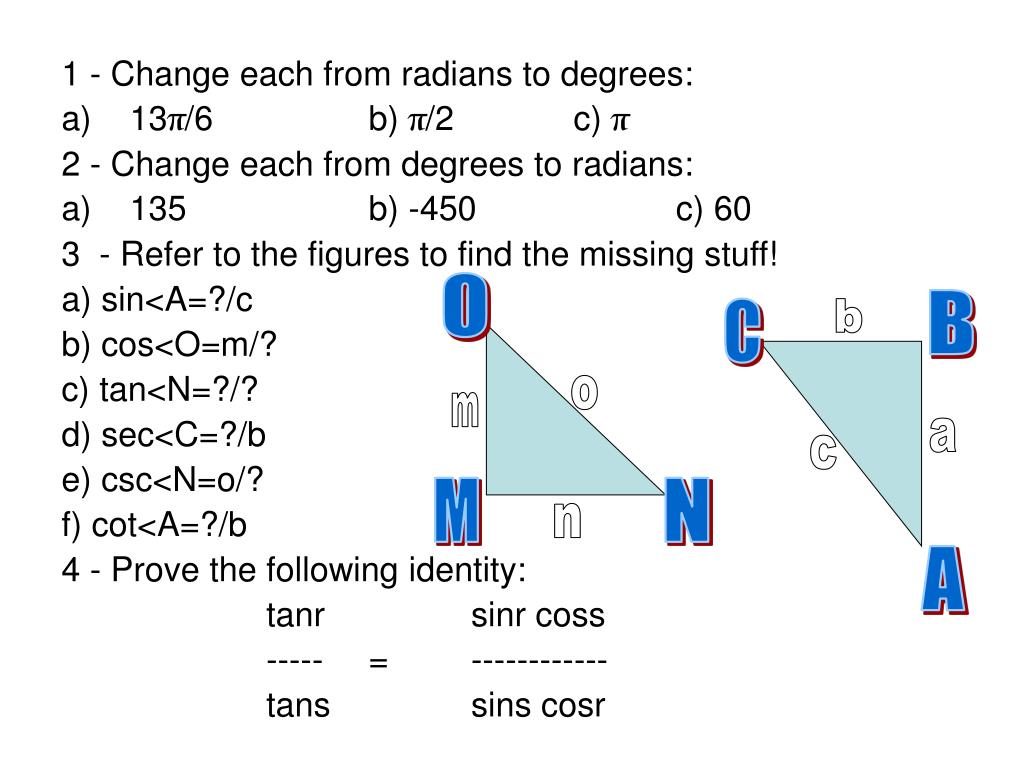



Ppt 1 Change Each From Radians To Degrees 13 P 6 B P 2 C P Powerpoint Presentation Id




Convert 2pi3 Radius Into Degree Measure
π/2 radians is equivalent to 90° To convert radians to degrees, we use the following fact relating radians to degrees π radians = See full answer below90 = π 2 radians 135 = 3π 4 radians 180 = π radians 30 = 6 radians 45 = 4 radians60 = 3 90 = 2 radians o o o o Your calculator should be able to work with angles measured in both radians and degrees Usually the MODE button allows you to select the appropriate measure When calculations involve calculus you should always work with radians π/2 in degrees π/2 in degreesLearn how to evaluate inverse of reciprocal trigonometric functions Recall that the reciprocal trigonometric functions is given by the ratio of 1 and the coWe just apply, or we evaluate each of these ratios at 45 degrees A cosine of 45 degrees is the square root of 2 over 2 Sine of 45 degrees is square root of 2



Degrees To Radians Conversion To Rad Inch Calculator




Arc Measure Formula How To Find Angle Measure Of An Arc Video
Convert from Radians to Degrees (5pi)/2 5π 2 5 π 2 To convert radians to degrees, multiply by 180 π 180 π, since a full circle is 360° 360 ° or 2π 2 π radians (5π 2)⋅ 180° π (5 π 2) ⋅ 180 ° π90°=π/2 radians=100grads Degree is the initial default angle mode for a standard scientific calculator and a programmable scientific calculator Changing the Angle Mode SVPAM, VPAM, fx4800P, fx5500LA, fx3650P, fx3950P etc Press MODE to cycle through screens on the display until the angle mode selection screen is appears




Sin 8 Sin 58 Sin 38 And 0 Lt 8 Lt P 2 Then What Is The Value Of 8 In Degrees Brainly In




Radians To Degrees Video Trigonometry Khan Academy




Explanation Of A 45 Degree 2d Rotation Matrix Mathematics Stack Exchange
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/10424623/tau.png)



Tau Day Is Here Celebrate Tau Not Pi As The True Circle Constant The Verge



1




Objectives After Completing This Section You Should Be Able To Pdf Free Download




Day 9 Hw 1 And 2 Find A Coterminal Angle Between 0 And 2 Pi Youtube
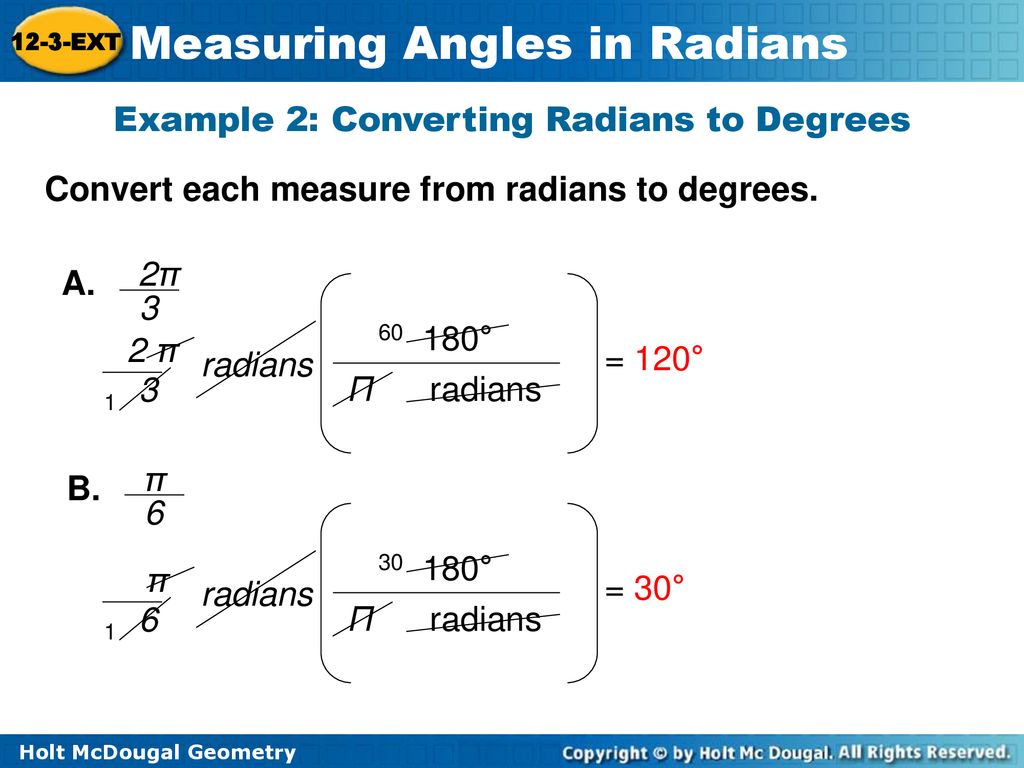



Measuring Angles In Radians Ppt Download



Pi Day Part 2




If An Angle Measures D Degrees Or C Radians Show That Frac D 90 Frac 2 C Pi




Radians To Degrees Formula Chart Converting Radians To Degrees




Angular Size Coe College




Graphical Representation Layer By Layer Of The Population Coding Download Scientific Diagram
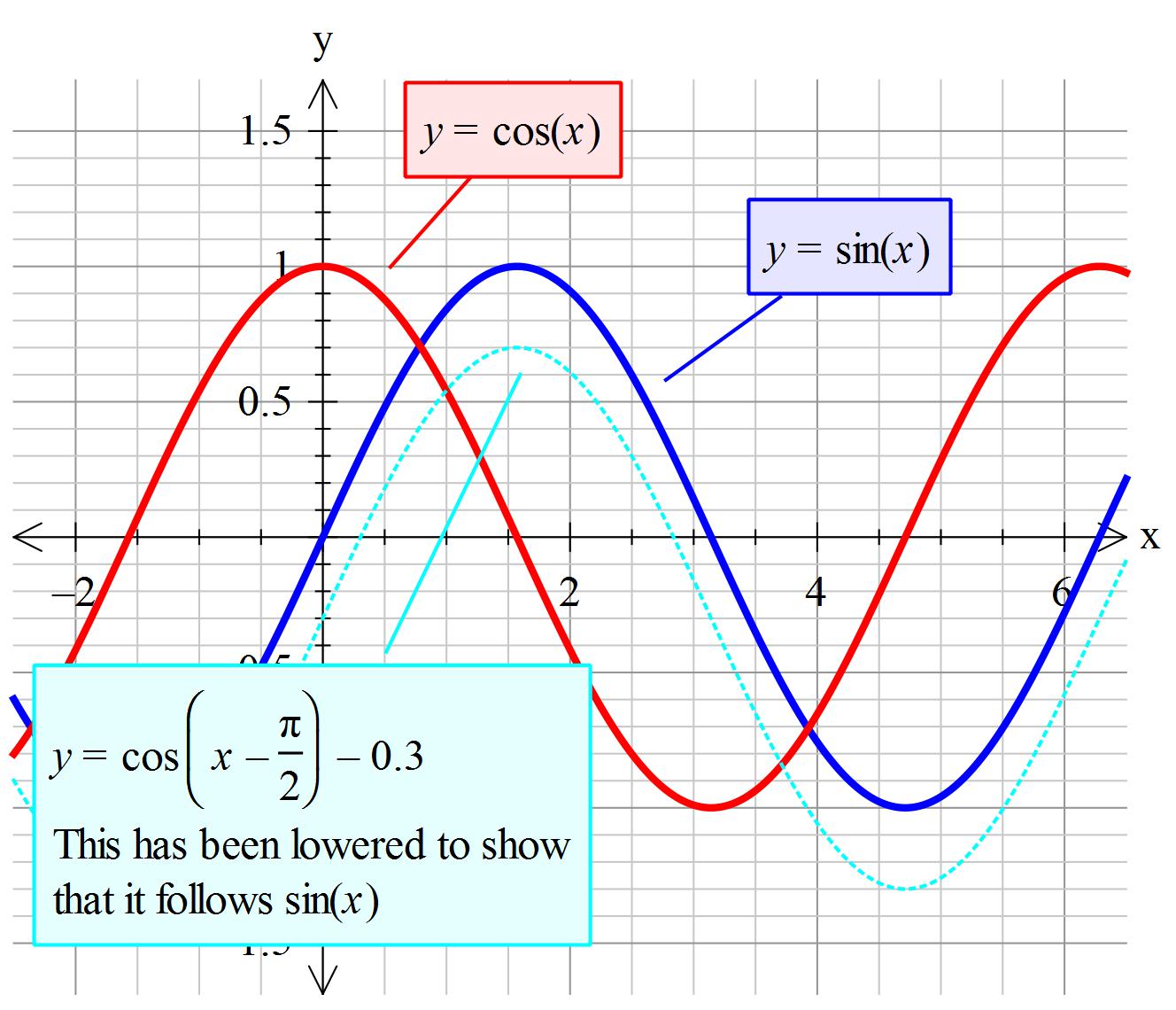



How Do You Prove Cos X Pi 2 Sin X Socratic




What Is Radian Solved Examples Trigonometry Cuemath




Trigonometric Functions Ppt Video Online Download



3




Convert 1 Degrees Into Radian 3 Points 180 Gauthmath




Compute Cos Pi 2 With The Unit Circle Youtube




Classifying And Constructing Angles By Their Measurement




I Need To Solve An Equation With Both Theta And Sin Theta In It How Do I Do It Mathematics Stack Exchange




42 Printable Unit Circle Charts Diagrams Sin Cos Tan Cot Etc
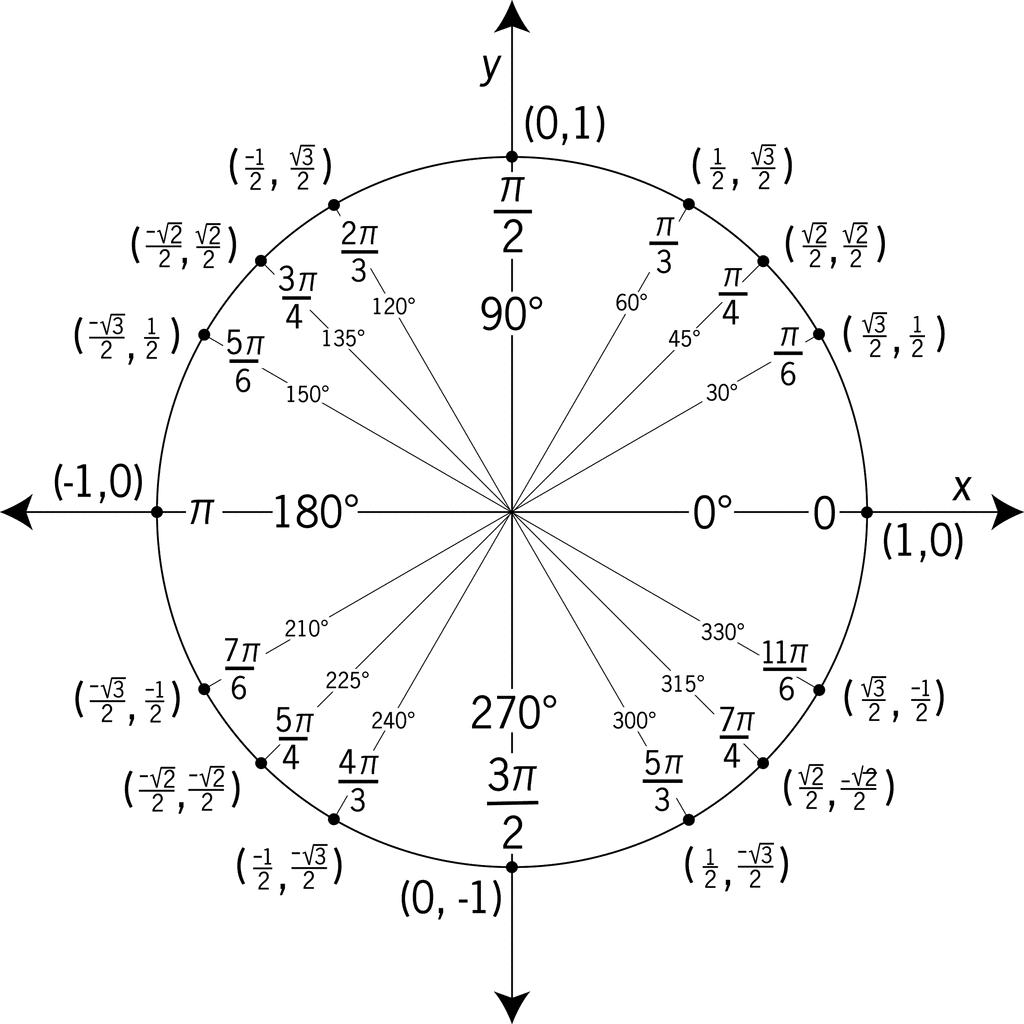



How Do You Find The Exact Value Of Cos 19pi 6 Socratic




How Do You Find The Exact Value Of Cos Pi 6 Socratic




1 3 Circle Skirt 1 Degrees Radian Is 2 P Circle Skirt Diy Sewing Pattern Circle




Radians To Degrees Video Trigonometry Khan Academy




Steradian Wikipedia




Angles Precalculus Ii




A Convert Each Radian Measure To Degrees 1 Frac Gauthmath




How To Study Math Trigonometry Study 101
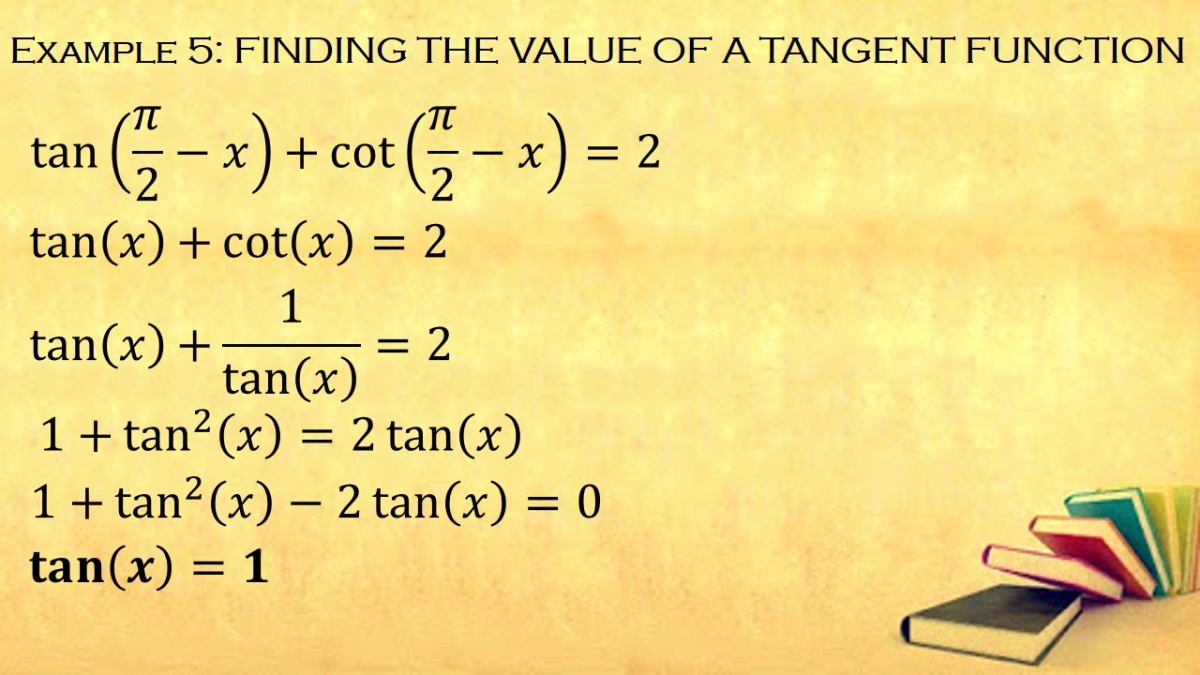



Cofunction Identities In Trigonometry With Proof And Examples Owlcation



Www Math Uh Edu Blerina Math1330f15 Complete Sec 4 2 Pdf
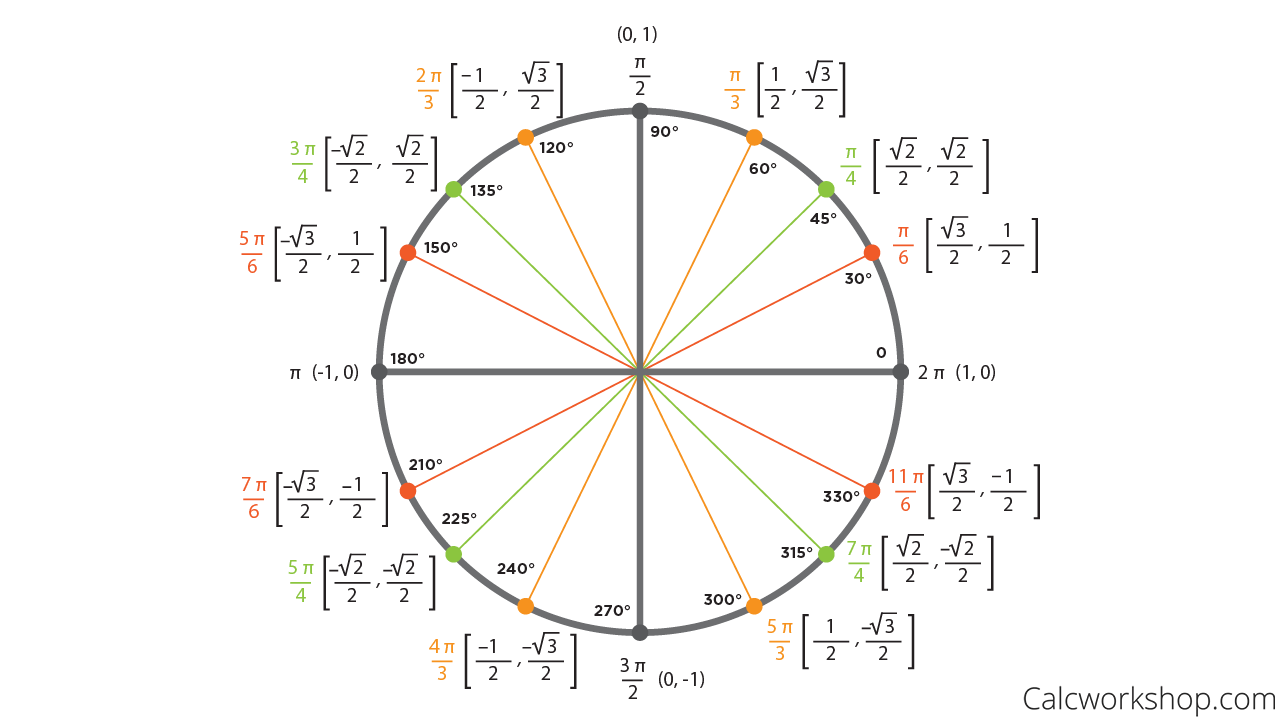



How To Convert Radians To Degrees 21 Amazing Examples



2 Change The Following Angles To Degrees A Gauthmath




Ex Sine And Cosine Values Using The Unit Circle Multiples Of Pi 6 Radians Youtube




Angles Precalculus Ii
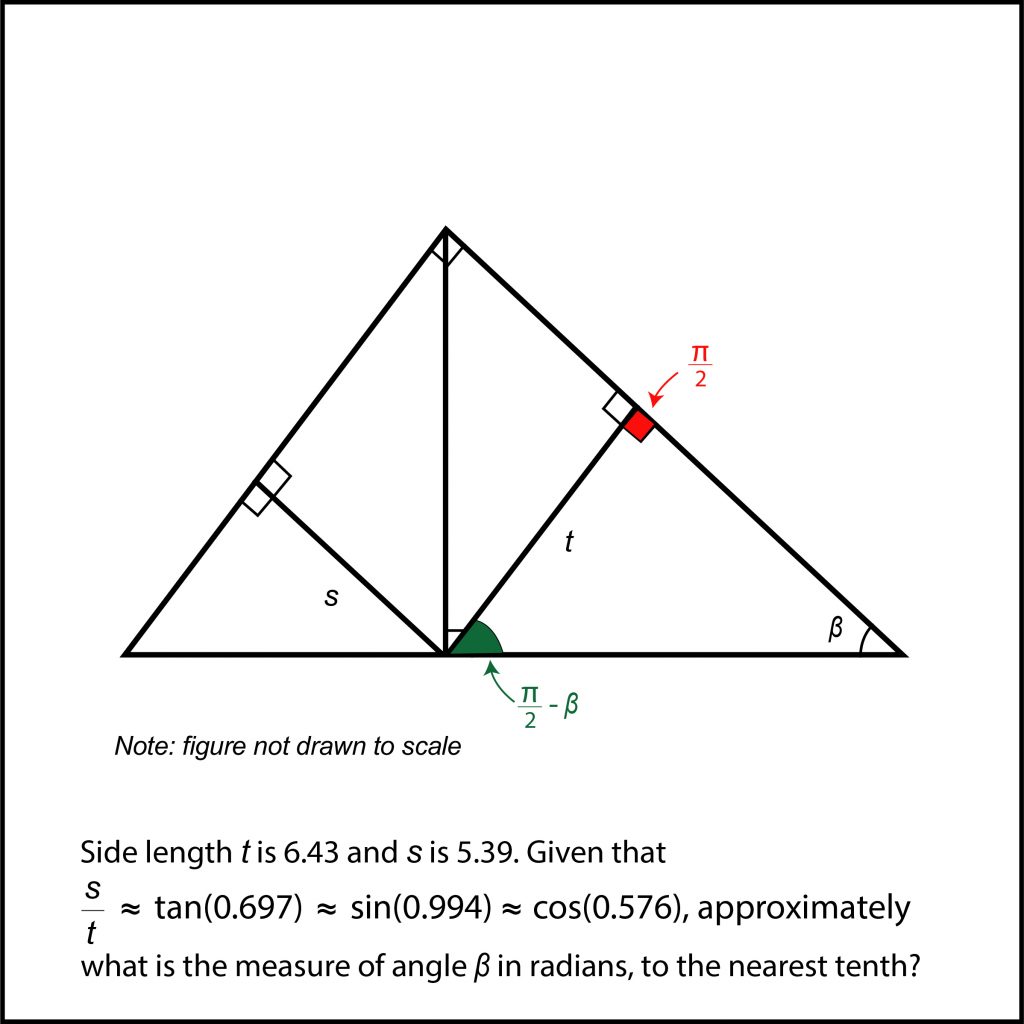



How To Solve Hard Sat Math Problems Right Triangle Trigonometry Part 1 Dan S Test Prep




The Unit Circle Ck 12 Foundation




5 Ways To Calculate Pi Wikihow




How Do You Find The Sine Cosine And Tangent Of 19pi 2 Radians Socratic




Degree Angle Wikipedia




What Is Math Sqrt Pi Math Quora




The Measure Of Central Angle Abc Is P 2 Radians What Is The Area Of The Shaded Sector Brainly Com



How To Calculate Arc Length Of A Circle Segment And Sector Area Owlcation



Radians And Degrees Youtube




Ex 3 1 2 Find Degree Of Radian Measures 11 16 4 Ex 3 1




There Are Exactly P Radians In A Semicircle There Are Exactly P Radians In A Full Circle There Are Brainly Com




Classifying And Constructing Angles By Their Measurement



1



Find Exact Value Of Cos 2 Pi 8 Youtube



Efisd Net Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid




How To Convert Radians To Degrees 4 Steps With Pictures




Find The Derivative Of F X Sinx At X Pi 2




Terminal Points On A Unit Circle Youtube
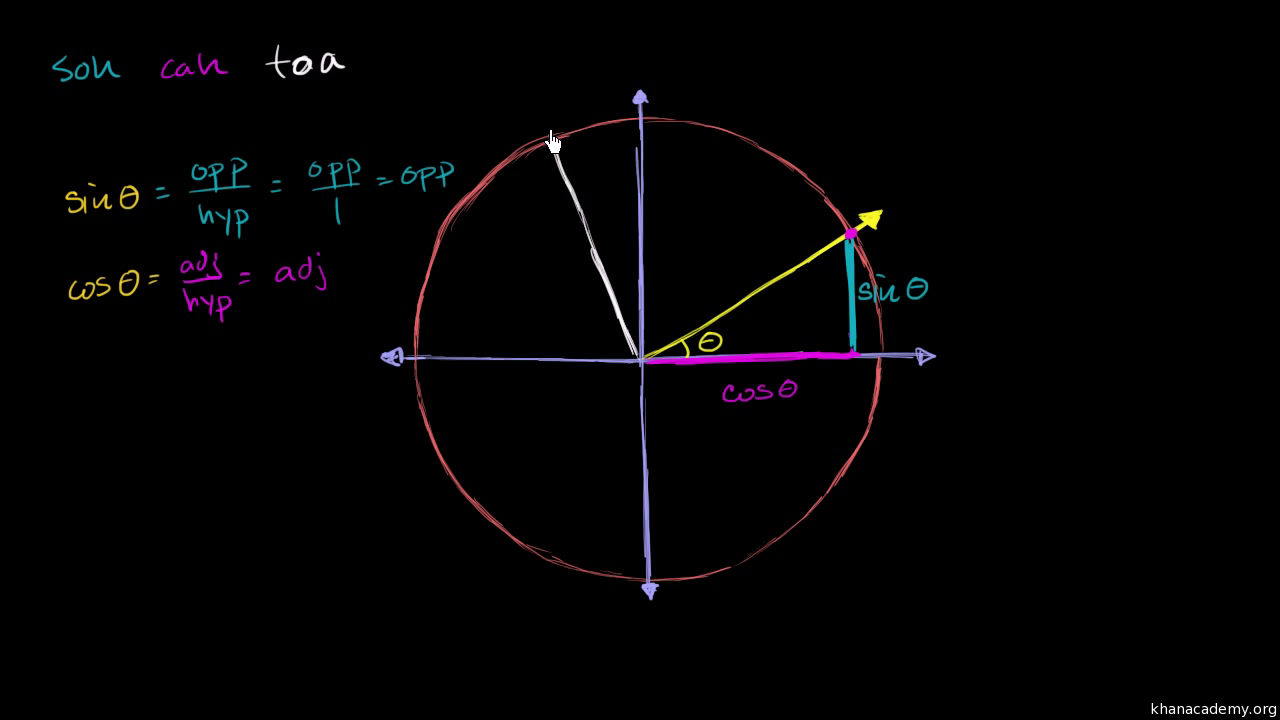



Sine Cosine Identities Periodicity Video Khan Academy




10 2 Angles And Their Measure Mathematics Libretexts




Reference Angle Cuemath



Www Math Uh Edu Blerina Math1330f15 Complete Sec 4 2 Pdf
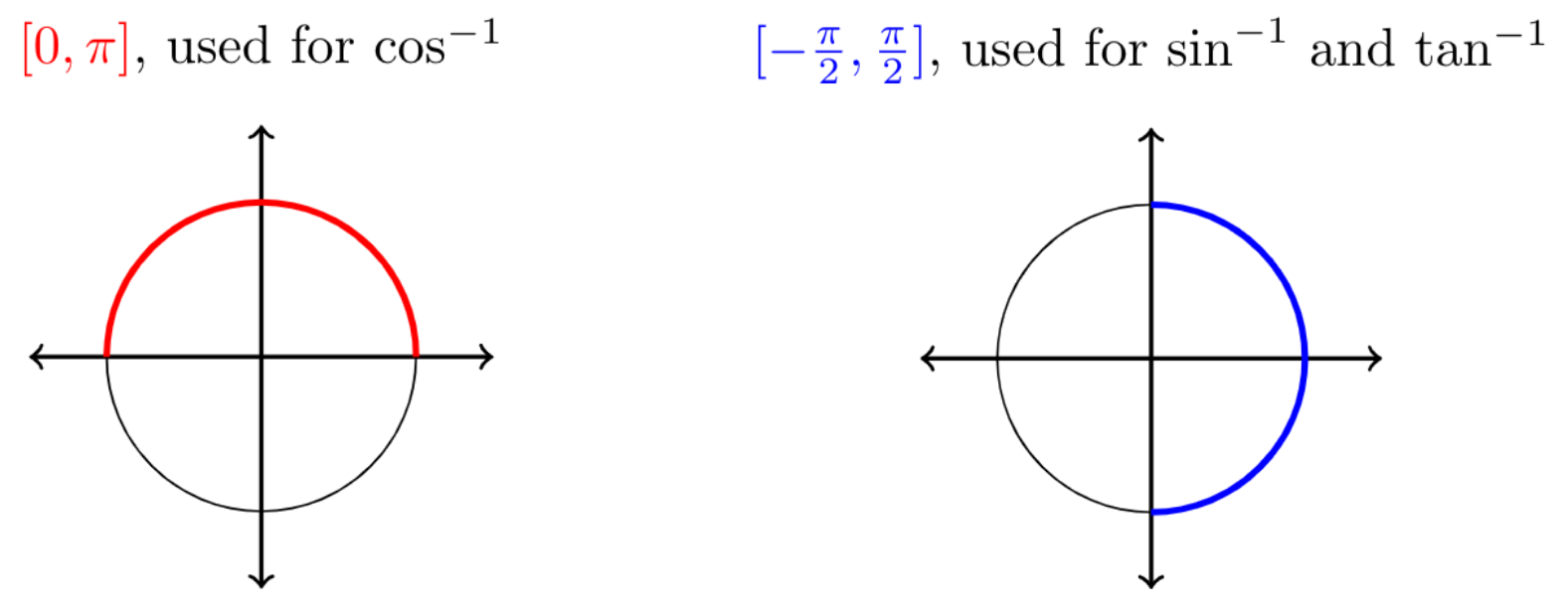



Mfg Inverse Trigonometric Functions



Pplato Flap Math 1 6 Trigonometric Functions



Http Mrsk Ca Ap Arclengthsectorareawordprob Pdf
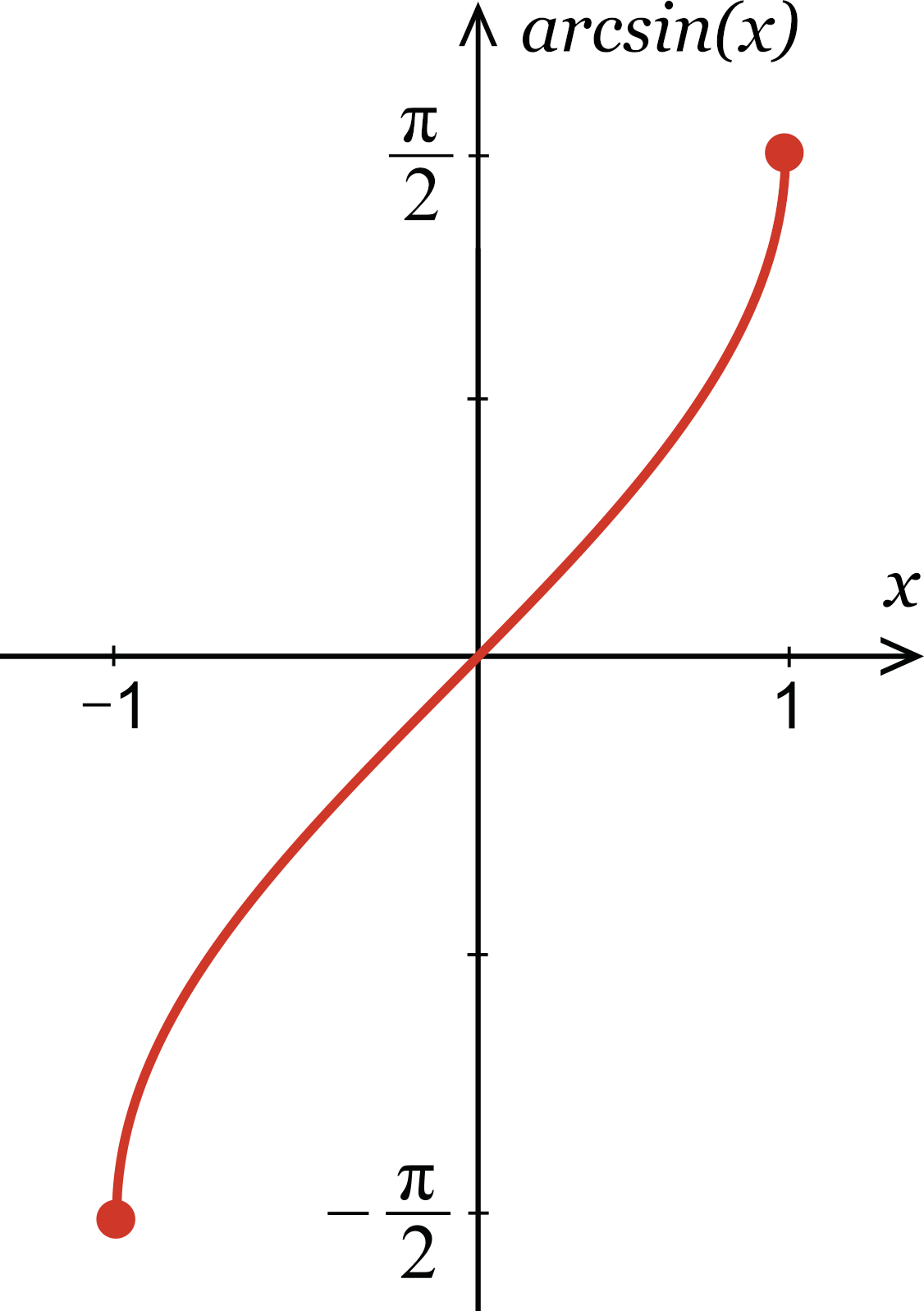



Inverse Sine Calculator Calculate Arcsin X Inch Calculator
/1280px-Circle-trig6.svg-5c850cc346e0fb0001a0be76.png)



Convert Angles From Radians To Degrees In Excel




Degrees And Radians J Verdejo Tips And Trigs




How 360 Degrees Is Equal To 2 Pi Radians Youtube
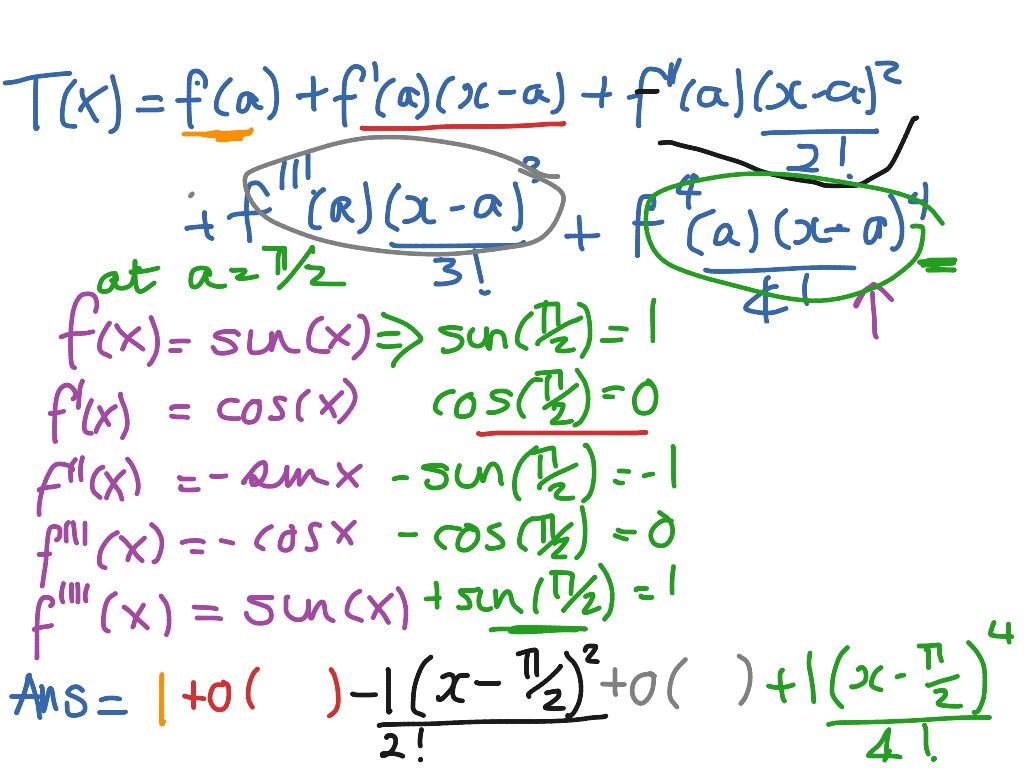



Taylor Series Of Sin X At Pi 2 Math Calculus Taylor Series Showme



Should Your Calculator Be In Radians Or Degrees For Physics Neoadviser
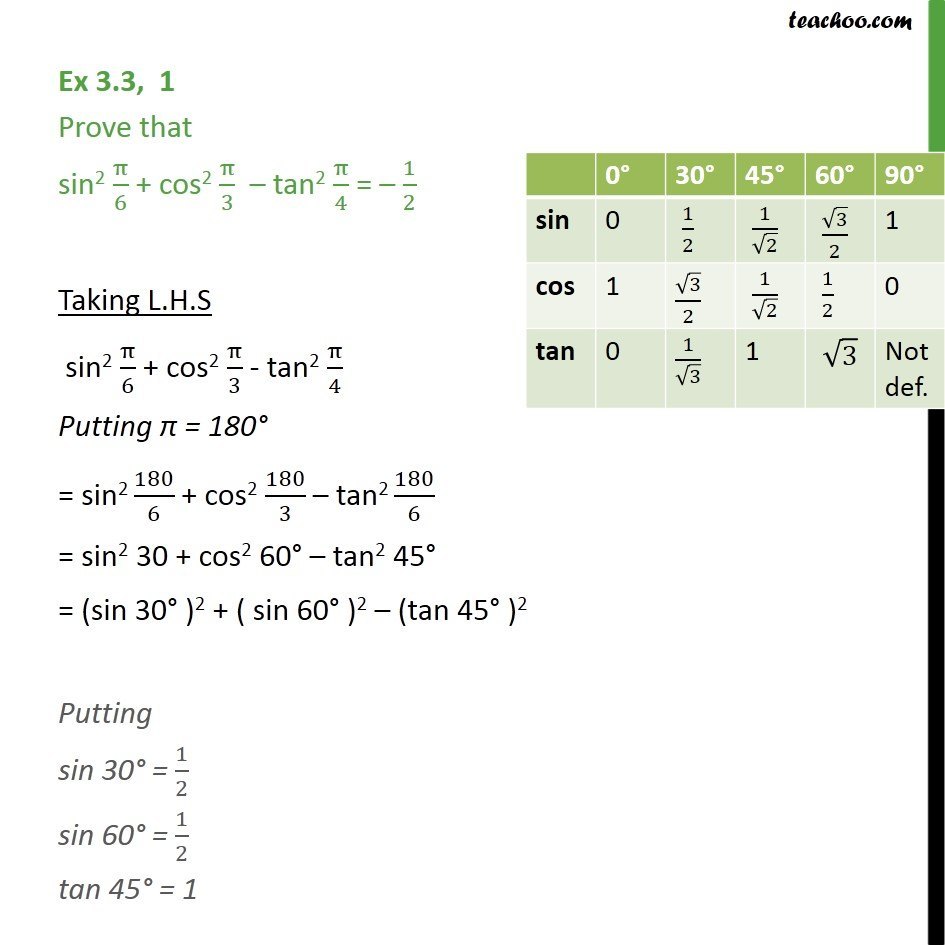



Ex 3 3 1 Prove Sin2 Pi 6 Cos2 Pi 3 Tan2 Pi 4 1 2




Convert The Following Radians Into Degrees I Fra Gauthmath




Unit Circle Calculator Find Sin Cos Tan
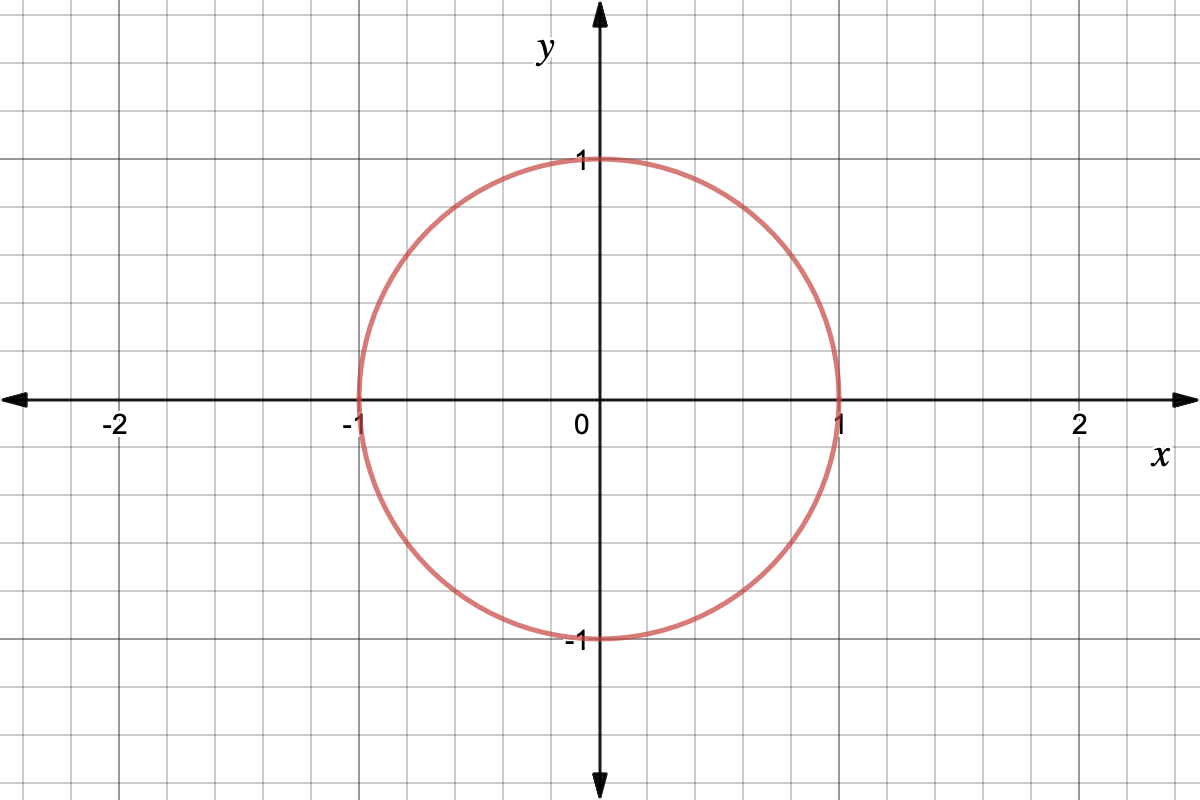



What Is The Unit Circle Expii
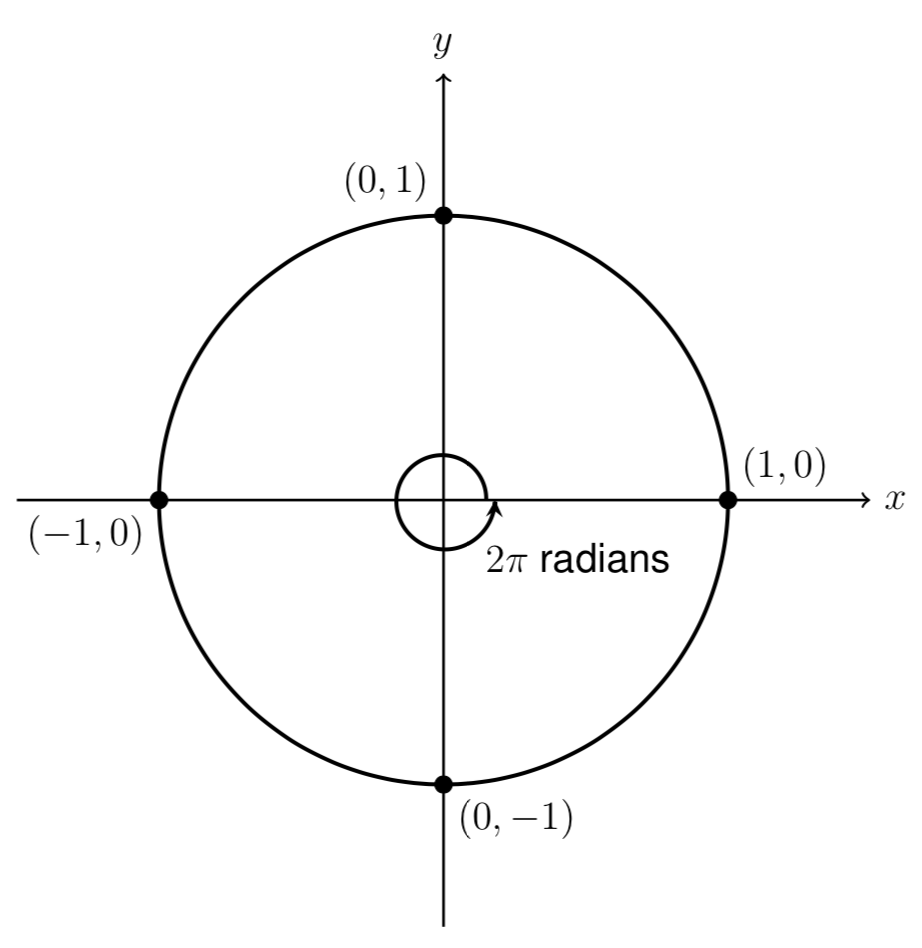



Mfg The Unit Circle




Converting Between Radians And Degrees Expii




How To Convert Degrees To Radians 5 Steps With Pictures
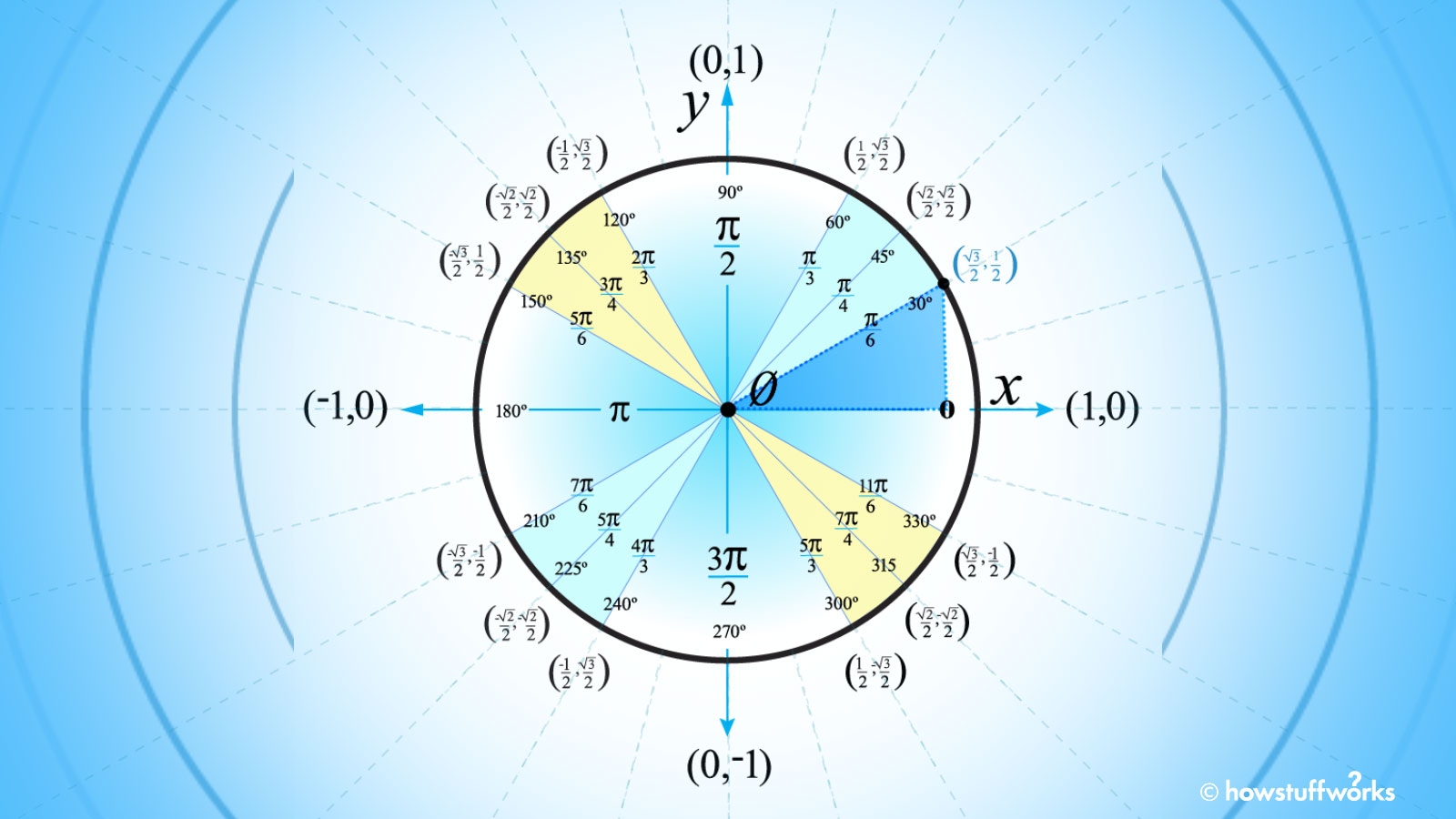



How To Use The Unit Circle In Trig Howstuffworks




Access Fractions And Greek Characters Strategic Finance
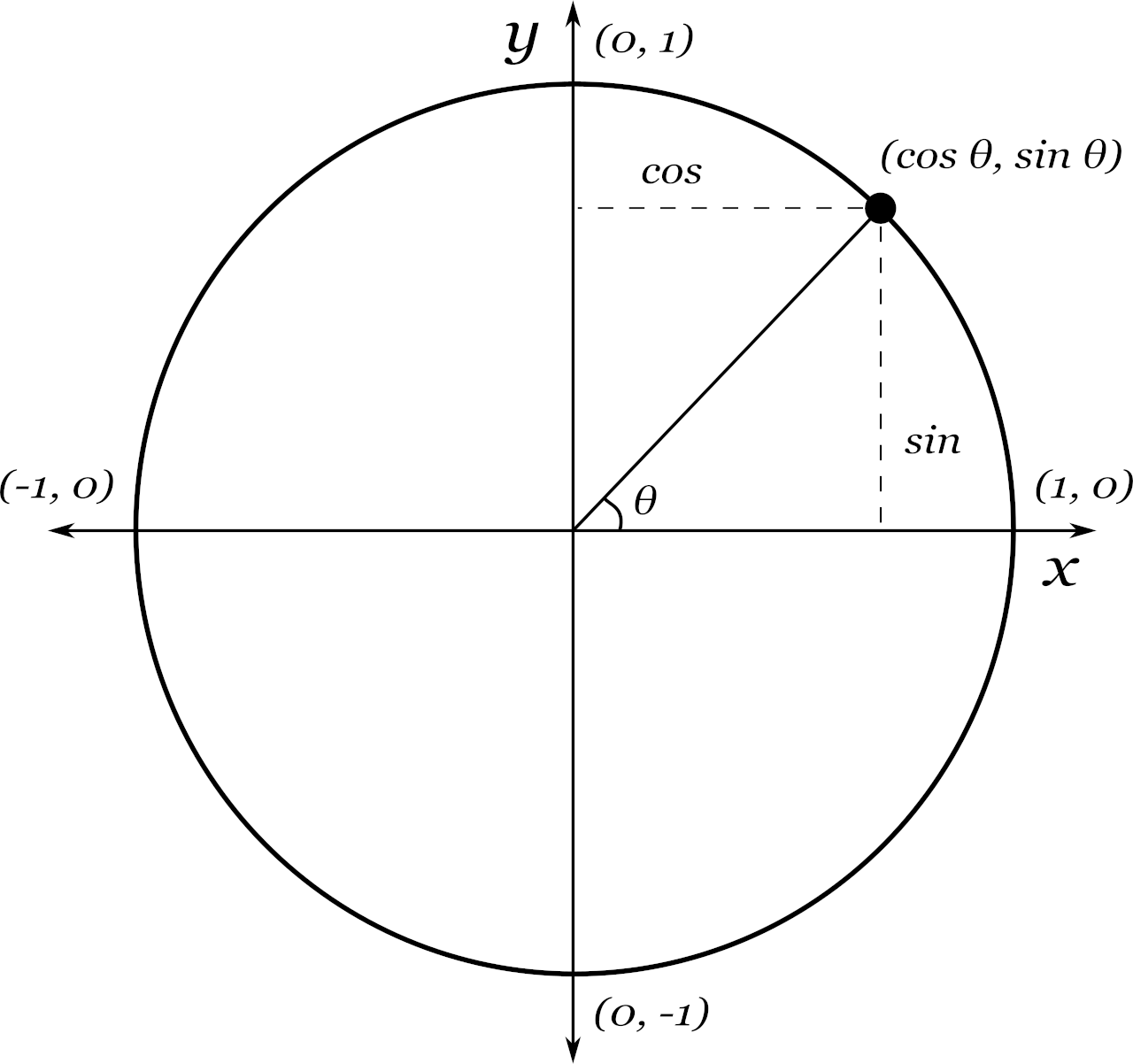



Unit Circle Calculator Inch Calculator
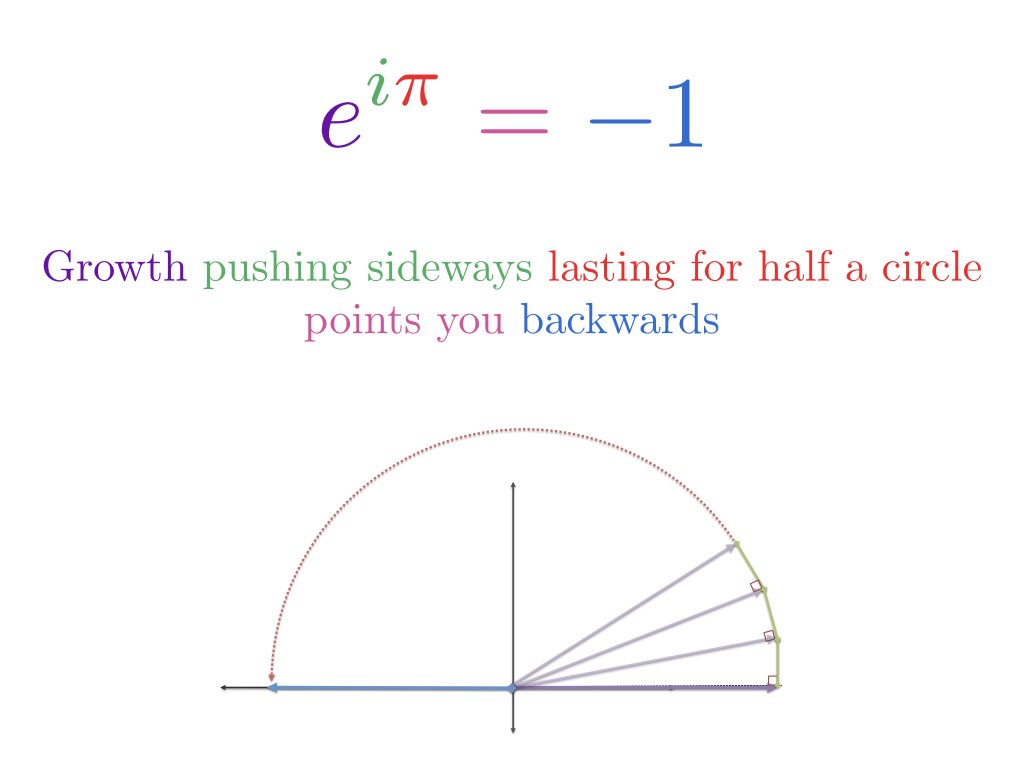



Intuitive Understanding Of Euler S Formula Betterexplained


