Derivation of w=mgh Asked by sanjeevrao2704 4th Jun, , 0843 AM Expert Answer If a body of mass m moves down from a height h, the force of gravity or weight acts on the body through a displacement h Thus, workUse the connection between force and potential energy to determine the general form of gravitational potential energy U = mgh applies only for a uniform field, so it does not apply here where the field goes as 1/r 2 F = dU/dr ΔU = ∫ F dr This gives U = GmM/r, if we define the potential energy to be zero at r = infinityAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators
Ppt Mechanics Of The Yoyo Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
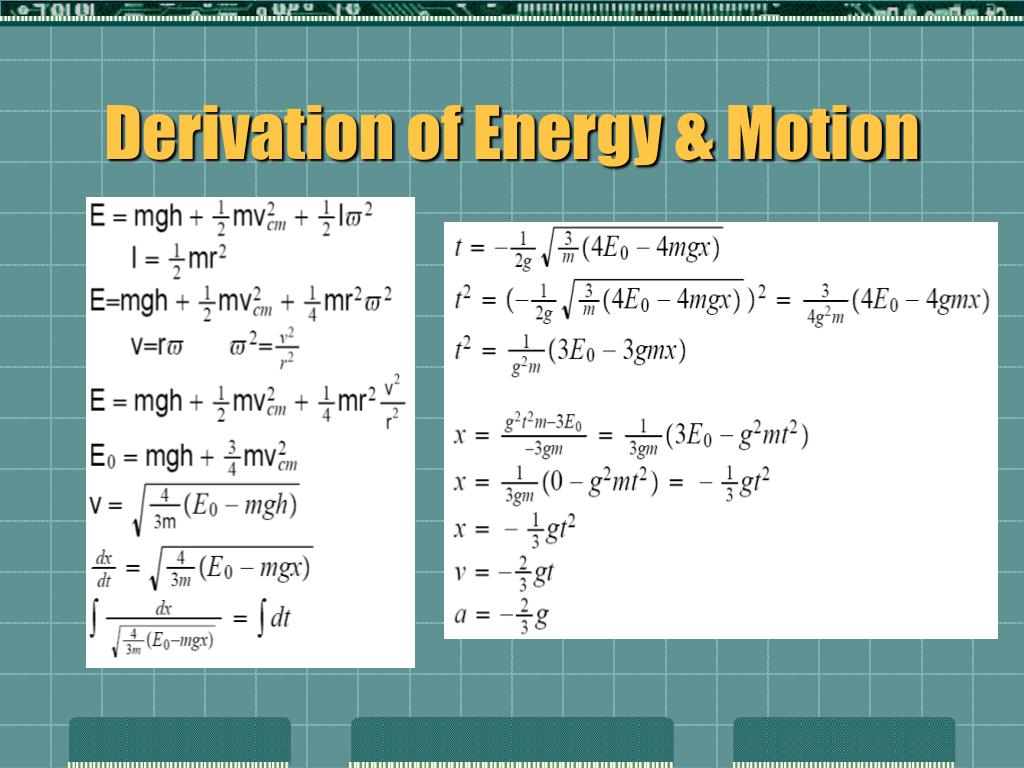
W=mgh derivation
W=mgh derivation-The formula mgh is valid for uniform gravitational field (constant g) which is an approximation of the real gravitational field of the Earth exactly for the case ePotential energy is the work done to take a body to a certain height For a body with mass m, h is the distance to which it is raised and g is the gravitational force acting on the body, then work done W is given as W = force * displacement W = mg * h ∴ W = mgh As the work done is equal to mgh which is gained by the object, potential




Law Of Conservation Of Energy Nishtha Vats Thesocialcomment
Answer To be specific,the work that you're talking about is the 'magnitude' of the work done by gravity on a body in raising it or dropping it through a height 'h' Now in general, the work done by any force 'f' in displacing a body through a certain displacement 'x' is given my Work=scalar proW = mgh Where, W = work done g = acceleration due to gravity h = height of free fall If the angle between gravitational force and direction of motion is 𝚹, then work done due to gravity is given by W = mgh cos 𝚹 So if an object is moving in horizontal direction on the surface of earth, then work done by gravity is 'zero' LLP is an abbreviation for many terms The terms vary from relating to science and medicine, to government and military To discern the term
W = force * displacement W = mg * h ∴ W = mgh As the work done is equal to mgh which is gained by the object, potential energy Ep is given as Ep = mgh Therefore, the above is the derivation of potential energy Stay tuned with BYJU'S for more such interesting articlesW = (Force)(Distance) = F D The footpound combines a unit of force a pound with a unit of distance a foot and is thereby a unit of work or energy 1 footpound is the amount of work that must be done to raise a 1 pound weight by 1 foot This also gives the change in potential energy of the 1 pound weightWhat does MGH abbreviation stand for?
It is also more convenient to divide the work into two terms 1) the flow workdone by the system which is p 2 v 2p 1 v 1, and 2) any additional work which we will term external work or shaft work, w s Then we have or We will call this the steady flow energy equation For an ideal gasdh=c p dT soThis video shows how to derive the equation W = mg This video is giving an examples of deductive reasoningDiscord is the easiest way to communicate over voice, video, and text Chat, hang out, and stay close with your friends and communities




Derive Derivation Of Kinetic And Potential Energy Pls Answer Fast Tomorrow Is My Exam Have A Brainly In




Derivation Of Law Of Conservation Of Energy Successforexam
(v) Work done by the force of gravity on a particle of mass m is given by W = mgh where g is acceleration due to gravity and h is height through particle one displaced (vi) Work done in compressing or stretching a spring is given by W = 1 / 2 kx 2 where k is spring constant and x is displacement from mean position W= FS =mgh or,the work W=mgh is done by the boy against the force of gravity Solution 18 The energy of a body is its capacity to do work Its SI unit is Joule (J) Solution 19 eV measures the energy of atomic particles 1eV= 16 x 1019 J Solution 1 J = 024 calorie Solution 21 Calorie measures heat energy 1calorie = 418 JMeaning MGH Massachusetts General Hospital MGH Mehr Generationen Haus (German MultiGenerational Home) MGH Mary Gates Hall (University of Washington) MGH




Give Me The Derivation Of Potential Energy As Fast As U Can Tomorrow Is My Exam Science Work And Energy Meritnation Com



Work Energy And Power Ppt Video Online Download
'Massachusetts General Hospital' is one option get in to view more @ The Web's largest and most authoritative acronyms and abbreviations resourceW X25X Mh/s W MTP Mh/s W Verthash Mh/s W Optional settings Cost $/kWh Calculate Compare the profitability and payback of all video cards in the Best Mining GPUs table Coin Mined Coins, 24h Revenue, BTC/24h Revenue, $/24h Profit, $/24h; Potential Energy is defined by the equation Ep = mgh so Ep = mgh Ep = (05)(981)(2) Ep = 981 Joules What is the potential energy of a 05kg bowl of soup sitting on a tray 2 meters above the




Work Energy And Power Icse Class 10 Physics Questions




Ap Physics 1 Finding Velocity In Terms Of Variables Through Co Derivation Of Energy Homeworkhelp
Answer (1 of 5) The classical gravitational potential is as follows V(r) = GM/r Where G is the universal gravitational constant, and M is the mass of the object causing the gravitational effect (for our planet, M is the mass of the Earth) For a simplified model of a perfectly spherical Ear Yuqing 218 0 The escape energy is given by where M is the planet mass, m is the object mass and r is the radius of the planet They set the energy raised in constant Earth's gravity equal to the escape energy The first equation given is derived using calculus I have seen a way of deriving it using the graph of the function and geometricW=mgh meaning W=mgh meaningW= Fd Work equals the applied force times displacement W= F g d The applied force equals the weight of the object (F = F g) W= mgd The weight of the object equals its mass times the acceleration due to gravity (F g = mg) W= mgh The displacement over which the work is done equals the height of the lift (d = h)In



What Is The Derivation Of Pe Mgh Quora




Gravitational Potential Energy Cie As Physics 19 21 Revision Notes
W = mg m = 100 g = 01 kg g = gravitational field strength g = 10 N/kg W = 01 kg x 10 N/kg W = 1 N So, a force of 1 N is the force need to lift an average sized apple off the ground The Wmg 1 Begin with the WorkEnergy Theorem The work that is done on an object is related to the change in its kinetic energy Δ K = W {\displaystyle \Delta K=W} 2 Rewrite work as an integral The end goal is to rewrite the integral in terms of a velocity differentialForms of kinetic energy translational, rotational and vibrational only simple examples



1




Education Is The Key To Success Physics Class X Chapter No 8 Questions And Answessc Part 1 And 2
Solution Gravitational mechanical energy is given by the expression, W=mgh Where, h=vertical displacement=5m m=mass of the item=40kg g= acceleration due to gravity= 98 m / s 2 Therefore, W=(40kg)(5m)( 98 m / s 2)= 1960J At halfway down the mechanical energy ofA negative potential energy is consistent with mgh for potential energy near the surface of the Earth If you lift an object a height h from the ground, the potential energy change is ΔU = U f U i = GmM/(Rh) ( GmM/R ) Now use the approximation (from Taylor's theorem)W gravity = mgh is the work done BY the gravity force F gravity = mg in the process of moving the mass m upward a distance h NUMERICAL EXAMPLE Suppose m=3 kg and h=5 meter then W gravity = 3kg ä98mês ä5m which works out to W gravity = 150 J where J=Joule is a unit of energy One Joule=Ntäm WHAT IS THE MEANING OF THIS MINUS SIGN?



1




Let Us Consider An Equation 1 2 M V2 Mgh Where M Is The Mass Of The Body V Its Velocity G Is The Acceleration Due To Gravity And H Is The Height Check
The direction and magnitude of the centripetal acceleration is given by a = w x ( w x r) = w x v 7 The constant angular velocity w = ( Q 0)/ (t 0) = Q /t In time t, both points 1 and 2 rotate through angle Q so both points have the same angular velocity ForDerivation of Gravitational Potential Energy Equation w = ∫ ∞ r G M m x 2 d x w Since, W = mgh Substituting the values in the above equation, we get W = 2 × 12 × 10 = 240 N The change in gravitational potential energy is equal to the work done by gravity Therefore, Gravitational Potential Energy= 240 JouleSimple and best practice solution for W=mgh equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand,



Arrive At The Relation U Mgh By Deriving The Expression For Gravitational Potential Energy Of Earth Snapsolve




Phy 101 Lecture 6 6 1 Work Done
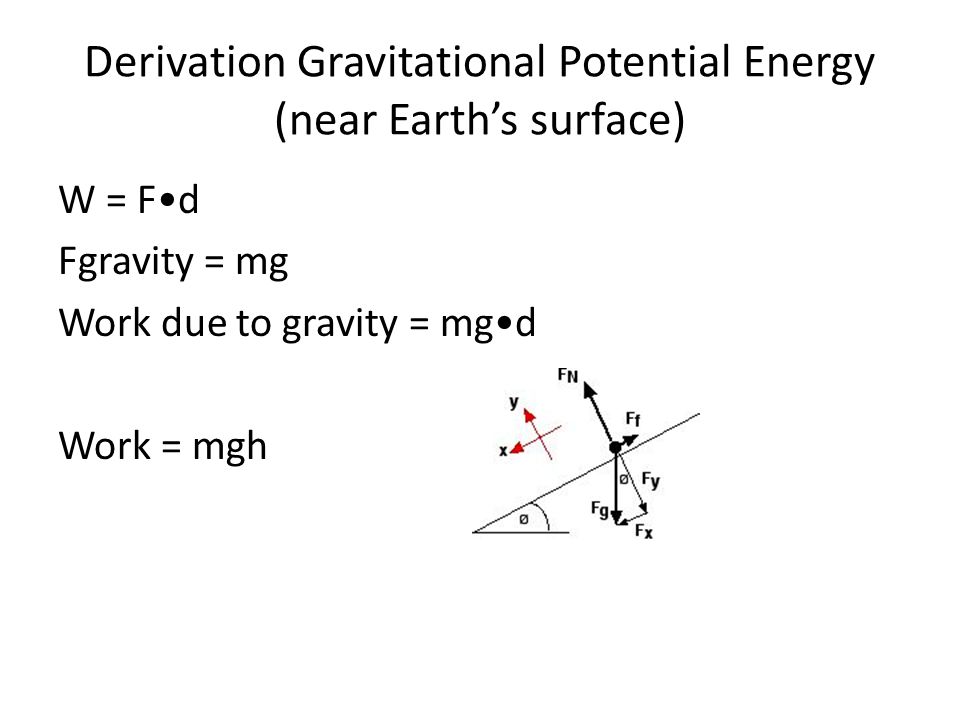
The work W done by a constant force of magnitude F on a point that moves a displacement s in a straight line in the direction of the force is the product = For example, if a force of 10 newtons (F = 10 N) acts along a point that travels 2 metres (s = 2 m), then W = Fs = (10 N) (2 m) = J This is approximately the work done lifting a 1 kgDerivation Substitution of Newton's second law (1686) into Coriolis' work principle (19) yields the following formula If, then, in the case of a weight lifted through a height or conversely descended through a height, the distance d becomes a measure of height h , and the acceleration a becomes the gravitational acceleration of earth gPE = mgh Calculate GPE for different gravity of different enviornments Earth, the Moon, Jupiter, or specify your own Free online physics calculators, mechanics, energy, calculators




Work Energy And Power Work What Is Work




Gravitational Potential Energy Derivations Formulas Examples
The work done on the mass is then W = Fd = mgh W = Fd = mgh size 12{ ital "W = Fd = mgh"} {} We define this to be the gravitational potential energy (PE g) (PE g) put into (or gained by) the objectEarth system This energy is associated with the state of separation between two objects that attract each other by the gravitational forceForms of kinetic energy translational, rotational and vibrational onlyMeaning MGH My Gothic Heart MGH My Guild Host showing only Slang/Internet Slang definitions ( show all 12 definitions) Note We have 46 other definitions for MGH in our Acronym Attic new search
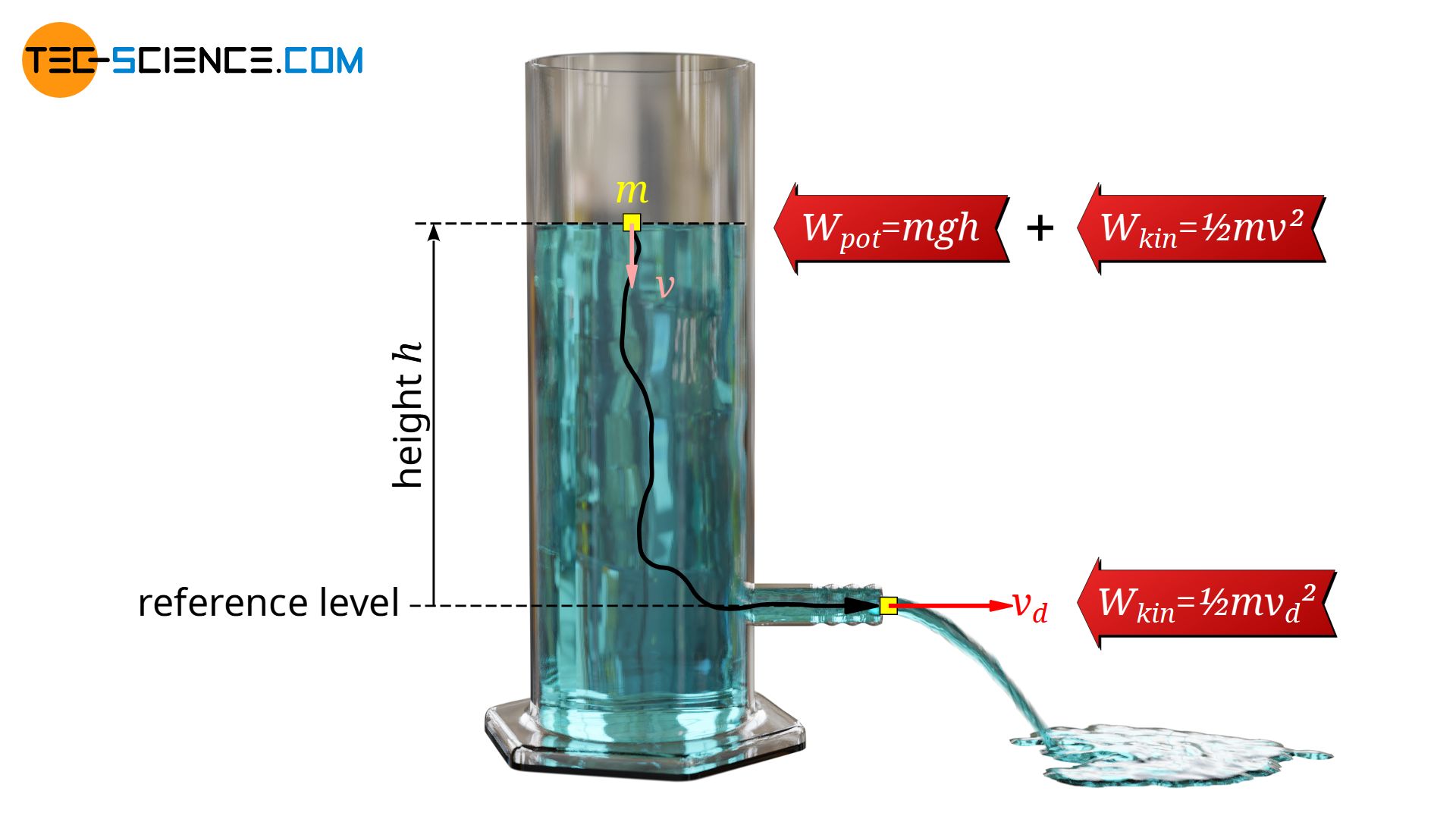



Discharge Of Liquids Torricelli S Law Tec Science




Work Power And Energy Notes Studypur
Find out what is the full meaning of MGH on Abbreviationscom!Calculate the unknown variable in the equation for gravitational potential energy, where potential energy is equal to mass multiplied by gravity and height;Work is the energy transferred into or out of a system through the action of a force Work done against gravity can be found using the equation Work equals Force times height or W = Fh Since F = mg we can use the equation W = mgh (m = mass, g



Energy Equation Fluids 35 Images Ppt Solved Fluids Problem Determine The Kinetic Energy Coeff 1




Plese Derive Potential Energy Which Is W Mgh Brainly In
Gravitational energy is the potential energy associated with gravitational force, as work is required to elevate objects against Earth's gravity The potential energy due to elevated positions is called gravitational potential energy, and is evidenced by water in an elevated reservoir or kept behind a dam If an object falls from one point to My form of derivation for KE Assume a mass at rest picks up speed after some time t Let u and v be initial and final speed of the mass Using kinematics, v^2 = u^2 2as u = 0 since mass is initially at rest Substitute F=ma into equation to get v^2 = 0 2s (F/m) mv^2 = 2Fs Fs = 05 mv^2 force (F) x distance (s) gives energy, so KE = 05 mvDerivation The gravitational In this case, a simple expression for gravitational potential energy can be derived using the W = Fd equation for work, so the work done in lifting it through a height h is the product mgh Thus, when accounting only for mass, gravity, and altitude, the equation is




Work When You Hold Something Are You Exerting




Wmgh Derivation
5 Leges Saxonum Lex Thuringorum Edictum Theoderici regis Remedii Curiensis episcopi capitula Lex Ribuaria Lex Francorum Chamavorum Lex Romana Raetica CuriensisIt is stationary It is higher up, thoughW= mgh Definition of energy, energy as work done Various units of work and energy and their relation with SI units erg, calorie, kW h and eV Definition (derivation included);



How To Derive The Formula Of Gravitational Potential Energy Mgh Dronstudy Questions



What Is The Derivation Of Pe Mgh Quora
W=mgh meaning W=mgh examples Saesipjos5r8y Looking for the definition of MGH?When the ball is at a height of 25 meters, the gravitational force has done an amount of work on the ball equal to W = mgh = 25 mg This work causes a change in velocity of the particle We now use the WorkEnergy Theorem, and solve for the final velocity mghLooking for the definition of MGH? PE = mgh, but this formula is only an approximation It assumes that g is constant, which it is not, it depends on altitude If you are at the height of the moon, g is very different But if we are sticking with heights that are relatively close to the ground, this formula works well




Cbse Class 9 Gravitational Potential Energy In Hindi Offered By Unacademy




What Is The Mathematical Expression Of Kinetic And Potential Energy Edurev Class 9 Question
W= mgh The displacement over which the work is done equals the height of the lift (d = h) Work Becomes Stored Energy This work which is done on the object as it is lifted does not end up as energy of motion, or kinetic energy, since, after the lift, the object is not moving;List of 74 best MGH meaning forms based on popularity Most common MGH abbreviation full forms updated in October 21Derivation Period of a Simple Pendulum Printer Friendly Version Simple pendulums are sometimes used as an example of simple harmonic motion, SHM, since their motion is periodic They also fit the criteria that the bob's velocity is maximum as it passes through equilibrium and its acceleration is minimal while at each endpoint But a deeper




Calculating Work Done On A Rigid Body Physics Stack Exchange
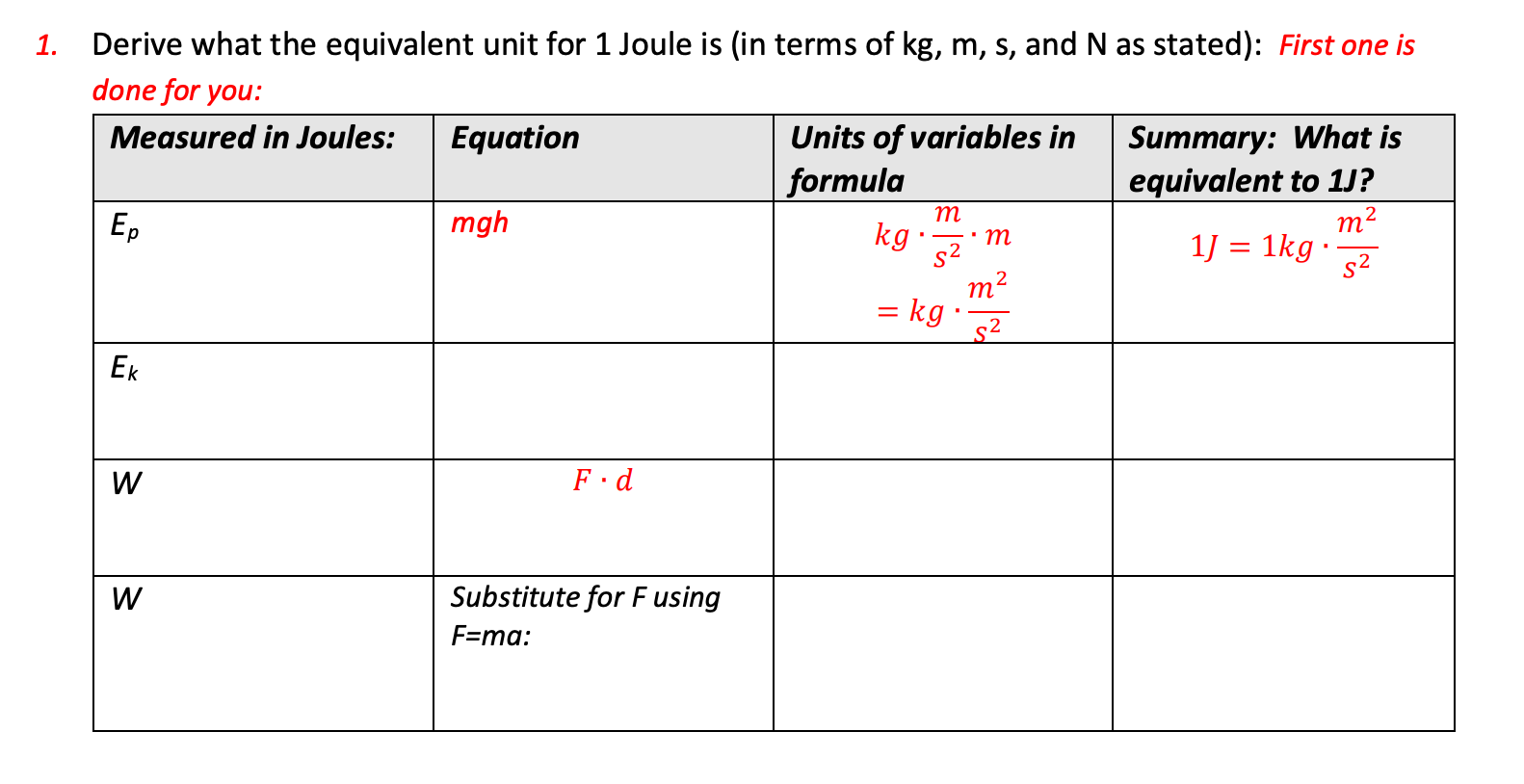



Solved 1 Derive What The Equivalent Unit For 1 Joule Is In Chegg Com
W= mgh Definition of energy, energy as work doneV arious units of work and energy and their relation with SI units erg, calorie, kW h and eV (derivation included);Ethereum (ETH) Ethash ETH BTC




Adamjee Coaching Work Power And Energy Question Answers Physics 10th




How We Prove That Mgh 1 2mv2 Youtube




Derive Expression Of Potential Energy Brainly In




Cbse Class 9 Law Of Conservation Of Energy In Hindi Offered By Unacademy




Http Www Nearingzero Net Nz 122 Jpg




Law Of Conservation Of Energy Nishtha Vats Thesocialcomment




Derivation Of Potential Energy P E Mgh Youtube




Wmgh Derivation




Energy1 Notes Pdf



1
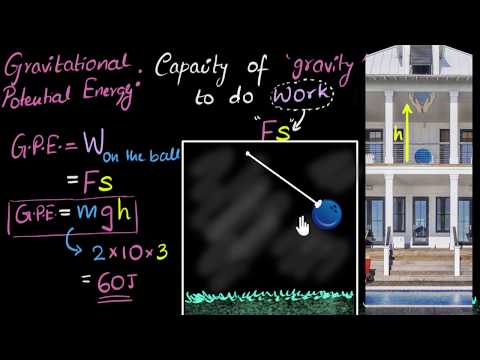



Gravitational Potential Energy Derivation Video Khan Academy



Co Contraction Of Ankle Muscle Activity During Quiet Standing In Individuals With Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Is Associated With Postural Instability Scientific Reports




Gravitational Potential Energy Equations The Change In Gravitational Potential Energy Of An Object Is Its Mass Multiplied By G And By The Change Ppt Download




Let Us Consider An Equation 1 2 M V2 Mgh Where M Is The Mass Of



Potential Energy




Ppt Mechanics Of The Yoyo Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
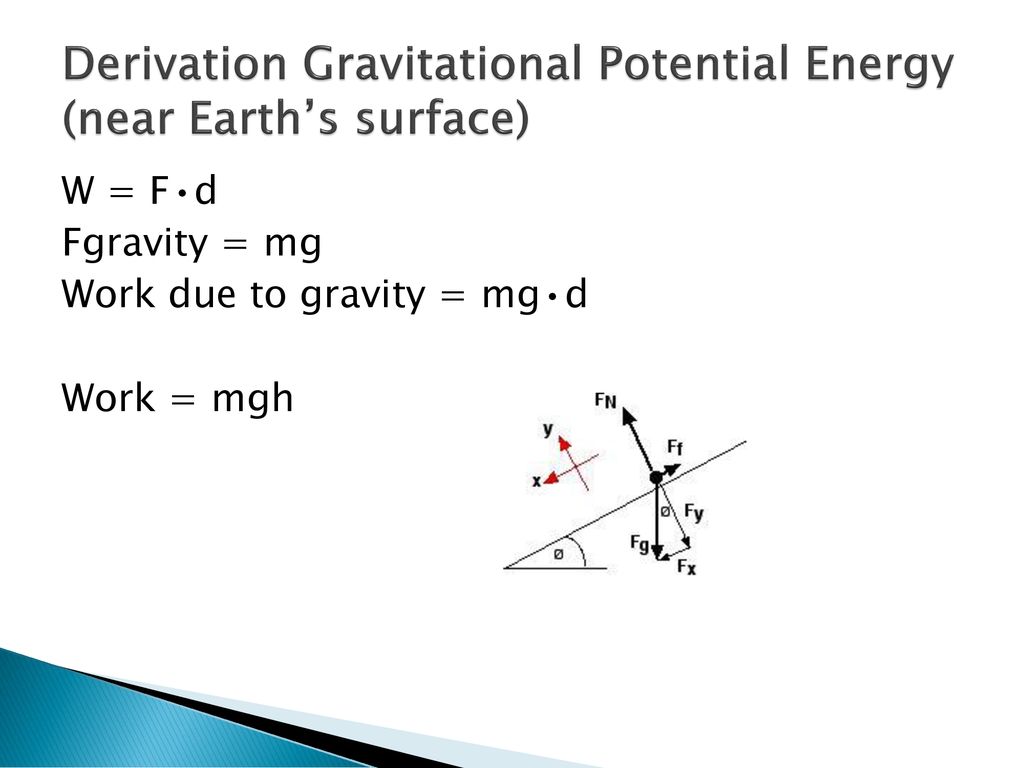



Work Energy And Power Ppt Download



Gravitational Potential Energy Geeksforgeeks
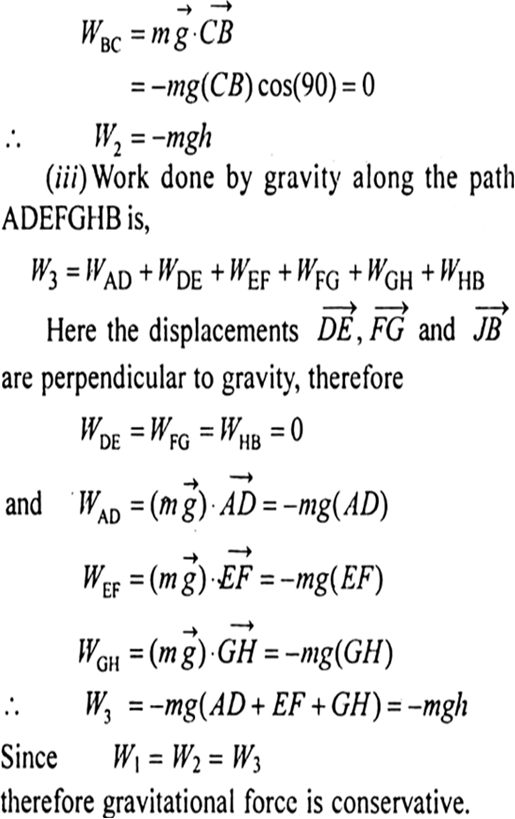



Show That Gravitational Force Is A Conservative Force From Physics Work Energy And Power Class 11 Haryana Board English Medium




Work When You Hold Something Are You Exerting




Derivation Of Change In Potential Energy Dp E Mgh Physics Smart Start Youtube




Law Of Conservation Of Energy Nishtha Vats Thesocialcomment
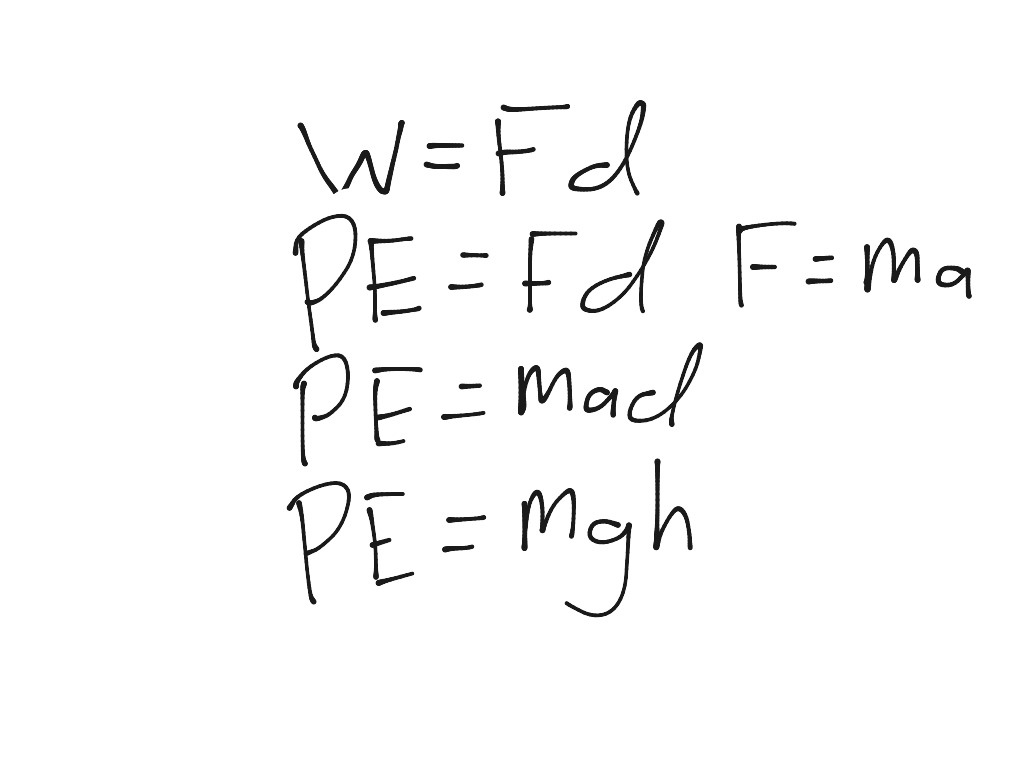



Deriving The Formula For Potential Energy Science Physics Kinematics Showme



Derive The Expression For Gravitational Potential Energy Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Derive An Expression For The Gravitational Potential Energy Above The Surface Of Earth Cbse Class 11 Physics Learn Cbse Forum




Physics 218 Lecture Xiv1 Physics 218 Lecture 14 Dr David Toback Ppt Download




Gravitational Potential Energy Derivations Formulas Solved Examples




Gravitational Potential Energy Cie A Level Physics Revision Notes



Physics Energy Maths Simplifying Wyzant Ask An Expert




Derive Gravitational P E U Mgh Physics Force Work Power And Energy Meritnation Com




Gravitational Potential Energy Reference From Planet S Surface Or Infinity



Mostly About Potential Energy



Derivation Of W Mgh Physics Topperlearning Com 4i0637ww



Work Energy And Power




P Mgh Derivation Youtube




Experts Can I Get List Of All Derivation Of Physics Till Work Energy Law Physics Work Energy And Power Meritnation Com




Class 9th Potential Energy High Time Study




Gravitational Potential Energy Cie As Physics 19 21 Revision Notes




Get Answer The Problem Reads I Understand How W Mgh Force Of Gravity X Transtutors




Phy 101 Lecture 6 6 1 Work Done
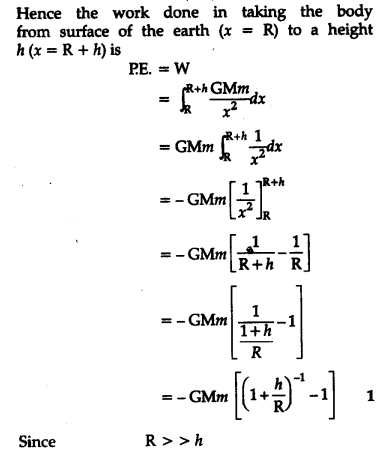



Derive An Expression For The Gravitational Potential Energy Above The Surface Of Earth Cbse Class 11 Physics Learn Cbse Forum




Chapter 8 Potential Energy And Conservation Of Energy Ppt Download



Potential Energy




Ith Watet Quid Is Way With Uniform Ac Mixed With Womghy Without Di Miled In W




Work Done By Gravity Path Independent Video Khan Academy




Derivation Of Potential Energy Class 9 Ncert Brainly In
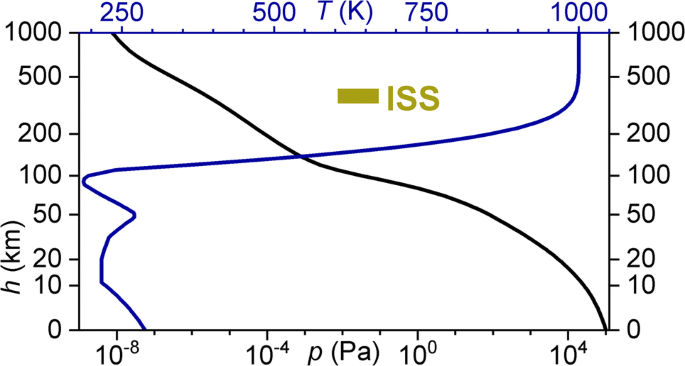



Barometric Formulas Various Derivations And Comparisons To Environmentally Relevant Observations Springerlink




Principle Of Conservation Of Energy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Check The Dimensional Correctness Of Relation Mgh 1 2 Mv Where Letters Have Their Usual Meanings



2




Power Formula Derivation Of Power Formula Examples




Gravitational Potential Energy Physics
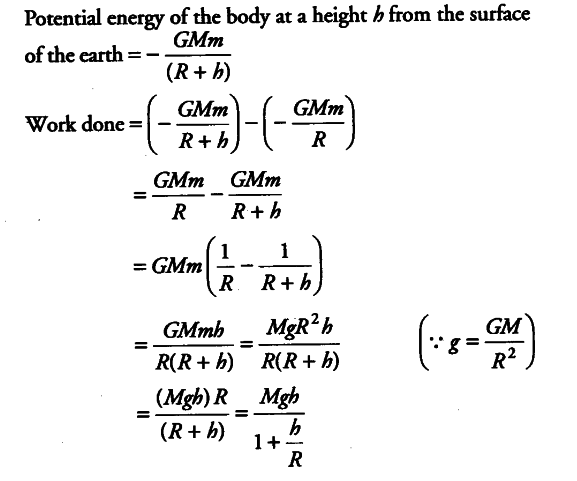



Derive An Expression For Work Done Against Gravity Cbse Class 11 Physics Learn Cbse Forum



Physicslab Gravitational Potential Energy




Derive Pe Mgh Brainly In




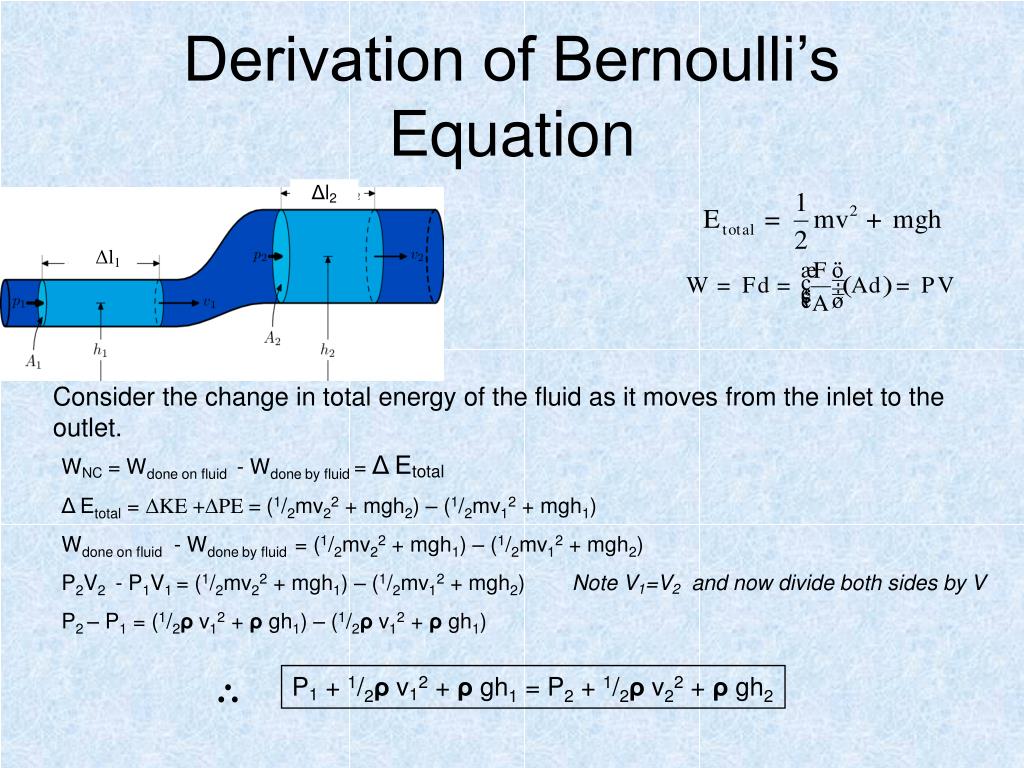
Bernoulli S Principle Ppt Download




Htpib06c Calculating Gravitational Potential Energy Using Ep Mgh Youtube
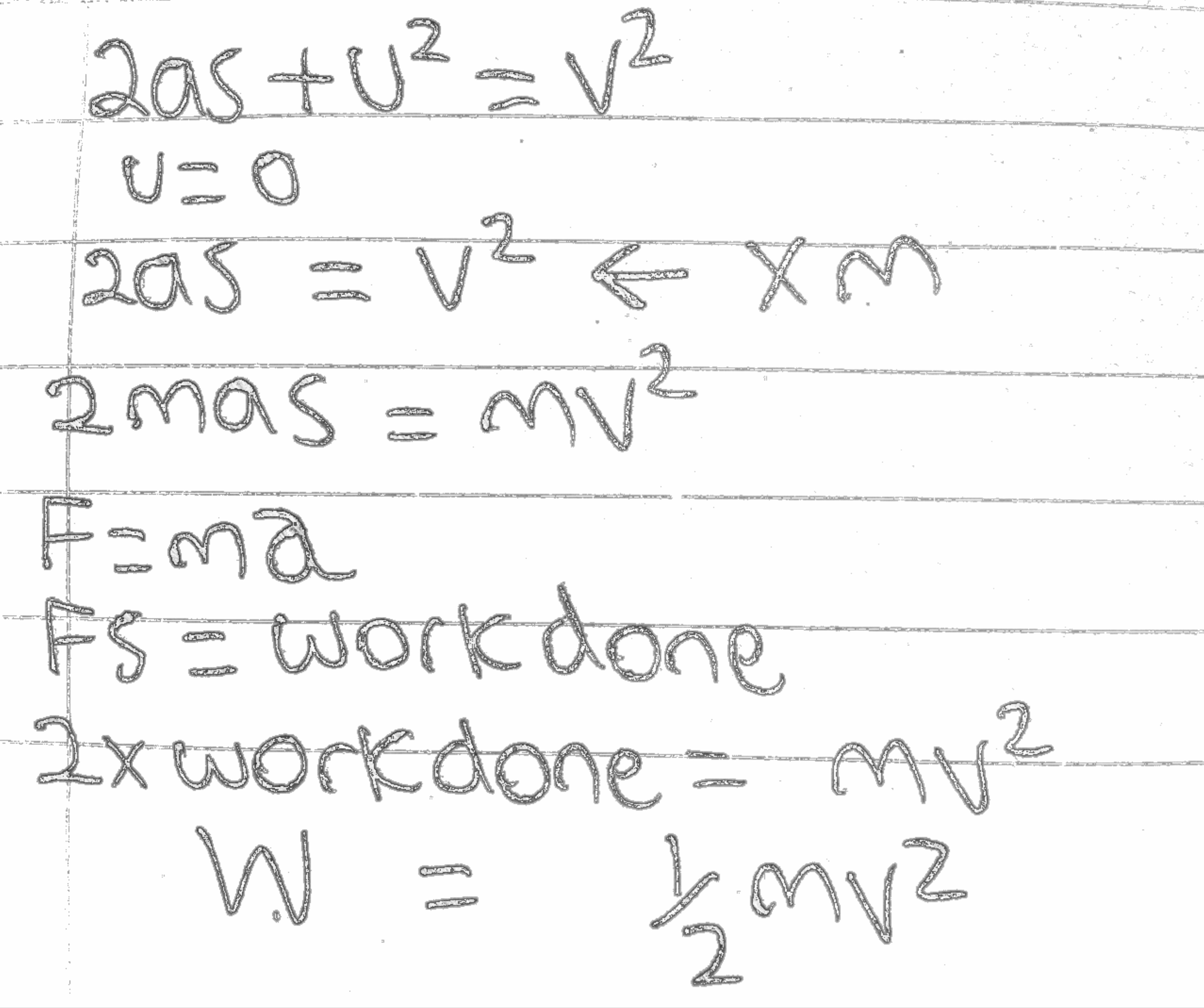



Energy Power Efficiency Revise Zone




Fastest What Are The Types Of Work Done




Work Power And Energy Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Notes




Prove Potential Energy P E Mgh With Figure Brainly In



1




Competition King Products



2




Gravitational Potential Energy Derivations Formulas Solved Examples
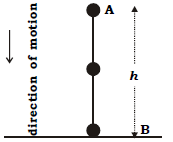



Work Energy And Power Icse Class 10 Physics Questions




Derivation Of Gpe Mgh Youtube




Navidi W Statistics For Engineers And Scientists Mgh 10 Isbn O 933s




Gravitational Potential Energy Derivations Formulas Examples




Bernoulli S Principle




Are The Gibbs Free Energy Curves Of Pure Substances Always Parabolic And If So Can Someone Point Me Towards A Proof Or Derivation Of This Fact




Chapter 4 Work Energy And Power




Gravitational Potential Energy Physics
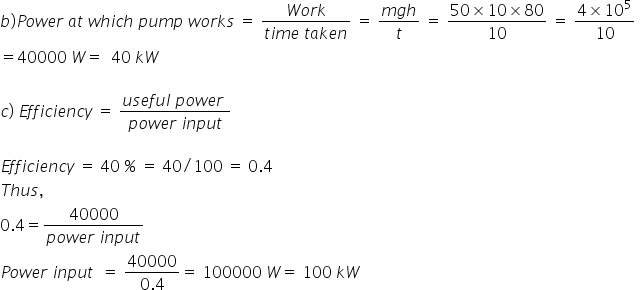



Ch Work Power Energy Physics Topperlearning Com 1unulpp




Ncert Exemplar Problems Class 9 Science Work And Energy Cbse Tuts




Education Is The Key To Success Physics Class X Chapter No 8 Questions And Answessc Part 1 And 2


